What is Edge Computing and Why Should You Care?

#image_title
Edge computing is a relatively new technology that has been gaining prominence in recent years. It refers to a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, typically near the edge of the network. This is in contrast to traditional centralized computing architectures that rely on a few large data centers located far away from the end-users.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a technology that helps to eliminate bottlenecks and reduce latency by bringing the processing and storage of data closer to the source, whether it is a device or a network endpoint. With edge computing, data is processed and analyzed locally, near the edge of the network, before being sent to the cloud or data center, where it can be further analyzed and stored for future use.
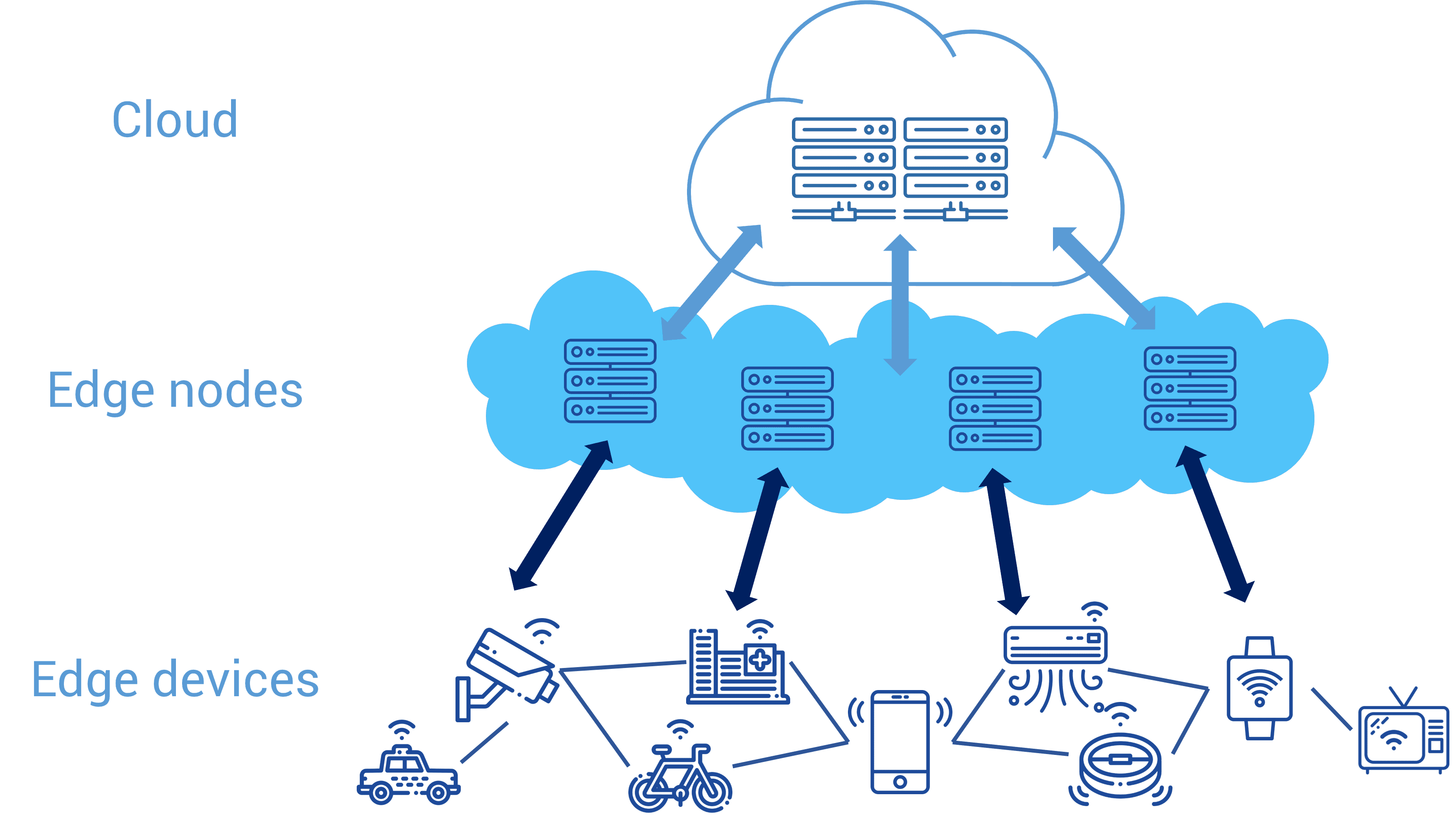
Advantages of Edge Computing
Edge computing has several advantages over traditional centralized computing architectures, including:
- Reduced latency: By processing data locally, edge computing can significantly reduce the time it takes for data to travel to and from a central data center or the cloud. This is particularly important for applications that require real-time data processing, such as self-driving cars or factory automation.
- Improved reliability: Edge computing architectures can be designed to be more resilient to network failures and outages, since they are not dependent on a single central processing resource.
- Greater scalability: Edge computing can enable greater scalability by distributing the processing load across many edge devices and endpoints, rather than relying on a central data center to handle all the processing.
- Increased privacy and security: Edge computing can provide increased privacy and security since data is processed and analyzed locally, reducing the need to transfer sensitive data to centralized data centers or the cloud. This can be particularly important for applications that handle sensitive data, such as medical or financial data.
Edge Computing: The Technological Trends’ Engine
Edge computing is a technology that is driving several technological trends, including:
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices has led to the need for edge computing architectures that can handle the processing and analysis of the vast amounts of data generated by these devices.
- 5G Networking: 5G networking is expected to drive the growth of edge computing by providing the low latency and high bandwidth required for real-time processing of data.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Edge computing can enable AI applications to be deployed locally, near the source of the data, rather than relying on centralized data centers or the cloud for processing.
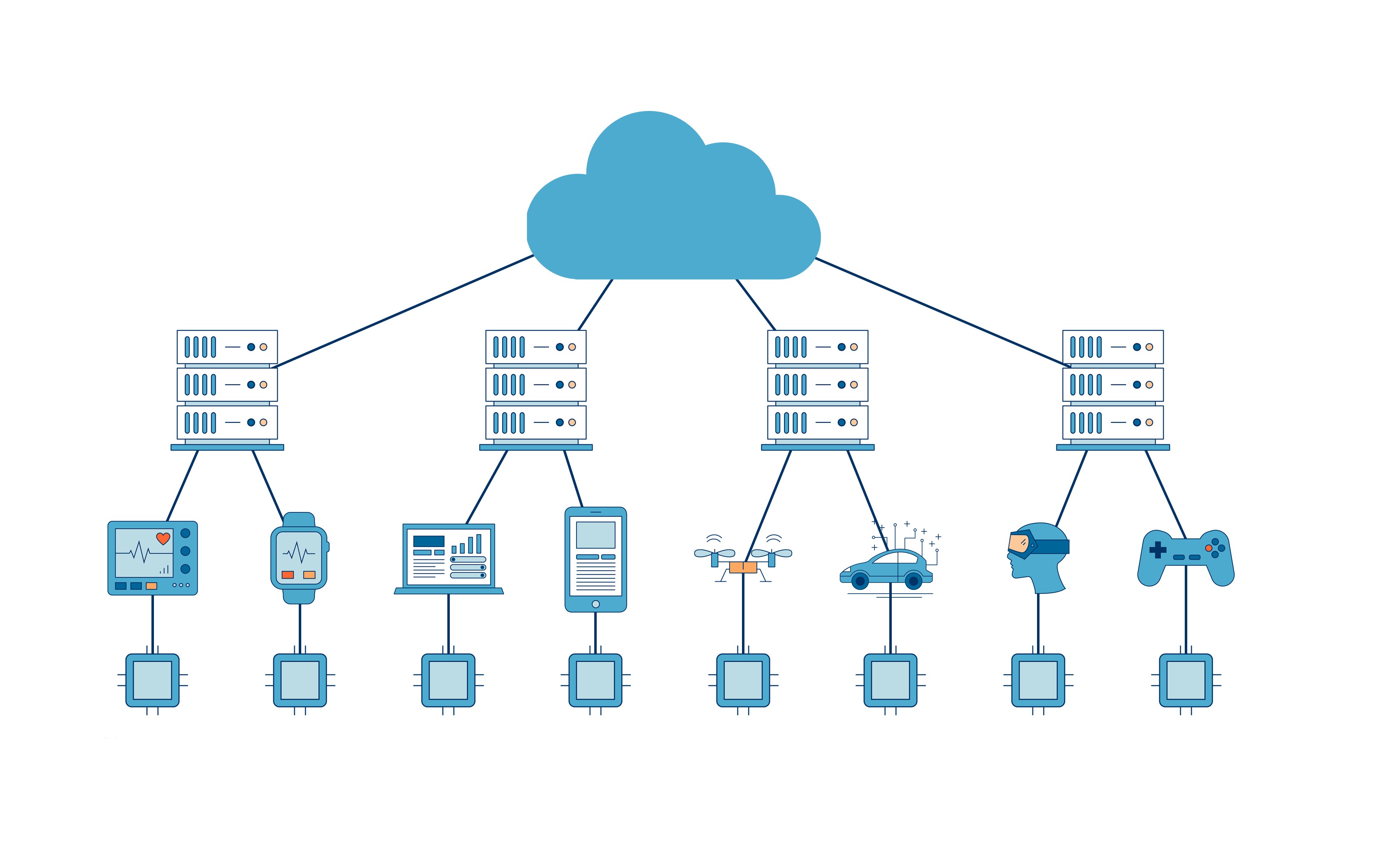
Abstract
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, typically near the edge of the network. It has several advantages over traditional centralized computing architectures, including reduced latency, improved reliability, greater scalability, and increased privacy and security. Edge computing is driving several technological trends, including IoT, 5G networking, and AI.
Introduction
In recent years, the growth of connected devices and the explosion of data generated by these devices has led to the need for new computing architectures that can handle the processing and analysis of this data. One of the most promising technologies that has emerged to meet this need is edge computing.
Edge computing refers to a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, typically near the edge of the network. This is in contrast to traditional centralized computing architectures that rely on a few large data centers located far away from the end-users.
Content
The advantages of edge computing over traditional centralized computing architectures are several. Firstly, edge computing significantly reduces latency by processing data locally. This is particularly important for applications that require real-time data processing, such as self-driving cars or factory automation.
Secondly, edge computing can improve reliability by leveraging a distributed architecture that is more resilient to network failures and outages. This is because edge computing is not dependent on a single central processing resource, unlike traditional centralized computing architectures.
Thirdly, edge computing can increase scalability by distributing the processing load across many edge devices and endpoints. This allows edge computing architectures to handle processing loads that would otherwise be impossible for a single central data center to handle.
Fourthly, edge computing can provide increased privacy and security since data is processed and analyzed locally, reducing the need to transfer sensitive data to centralized data centers or the cloud. This can be particularly important for applications that handle sensitive data, such as medical or financial data.
Edge computing is also driving several technological trends, including IoT, 5G networking, and AI. The proliferation of IoT devices has led to the need for edge computing architectures that can handle the processing and analysis of the vast amounts of data generated by these devices.
5G networking is expected to drive the growth of edge computing by providing the low latency and high bandwidth required for real-time processing of data. And edge computing can enable AI applications to be deployed locally, near the source of the data, rather than relying on centralized data centers or the cloud for processing.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a promising technology that is poised to revolutionize the way we process and analyze data. It has several advantages over traditional centralized computing architectures, including reduced latency, improved reliability, greater scalability, and increased privacy and security.
Edge computing is driving several technological trends, including IoT, 5G networking, and AI, and is expected to play an increasingly important role in the future of computing. As more and more devices become connected and more data is generated, the need for edge computing architectures that can handle the processing and analysis of this data will only continue to grow.

Source image : www.alibabacloud.com

Source image : ignasisayol.com
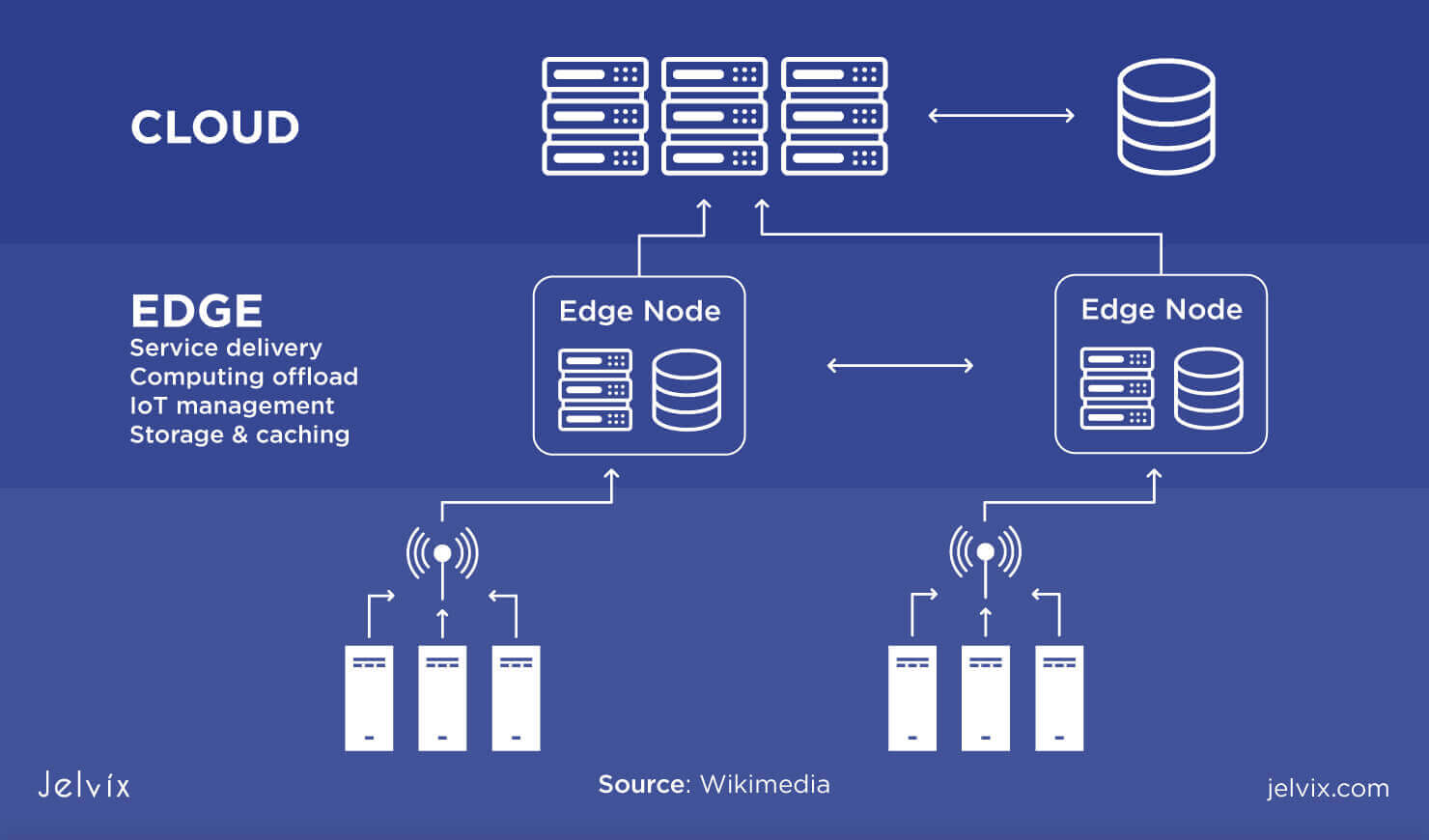
Source image : jelvix.com


