Using Virtual Reality in Healthcare: Training

VR Medical Training – Touchstone Research
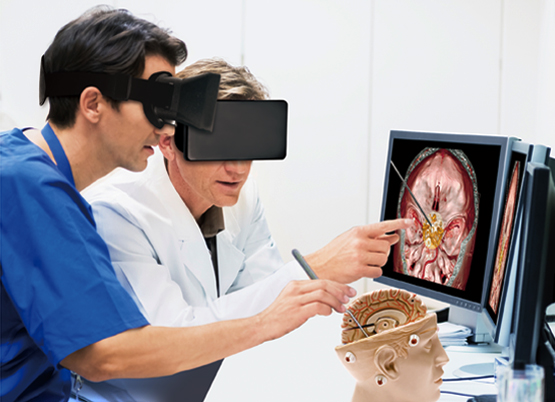
Abstract: Virtual Reality (VR) has emerged as an innovative tool in the field of medical training. The Touchstone Research conducted a study on how VR medical training can improve the skill set of the surgeons and medical professionals without actually operating on a patient. The study found VR to be an effective solution for providing hands-on training in a risk-free environment.
Introduction: Medical education and training have a crucial role in ensuring quality healthcare services. Medical professionals require years of education and training to become proficient in their field. A major fraction of medical training is hands-on practice, which traditionally involves working with real patients. However, this poses a range of risks for both the patient and the inexperienced trainee practitioner. Goldenberg et. al. (2016) highlight the high mortality and morbidity rate in the operating room, primarily due to the lack of training opportunities for medical professionals.
Content: Traditional medical training practices rely heavily on training in the real-world environment, where trainees witness and practice procedures under the observations of experienced professionals. This method of training is expensive, time-consuming, and may not provide enough opportunities for practicing rare or complicated procedures. However, advancements in the field of technology have introduced a new way of training medical professionals through VR.
A study conducted by Touchstone Research found that VR medical training can improve the skill set of surgeons and medical professionals without the need for actual surgery. The study involved a VR training program that mimicked a complex surgery involving a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The training program positively impacted the learning capabilities of residents, with improved skill sets, and lower complications observed in the real surgeries they performed .The study established the benefits of introducing VR in the curriculum of medical training, stating it to be an effective solution to provide hands-on training in a risk-free environment.
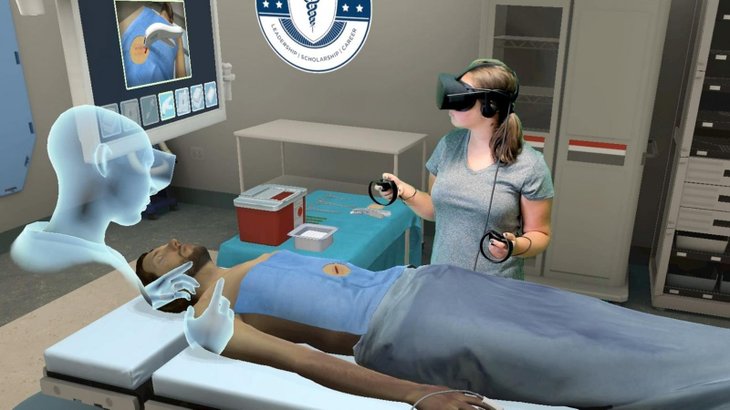
VStream Digital Media, in partnership with Western Sydney University (WSU), introduced the use of VR to train medical professionals on how to conduct anesthesia care for patients. The VR training allows trainees to experience and prepare for situations that are rarely experienced by trainees in the real world. The VR program provides a risk-free environment to train anesthesia procedures like needle and catheter insertion, cuff inflation and deflation, and pulse oximeter readings. The training program aims to expose trainees to situations that would be difficult to recreate under other training scenarios.
Dr. Richard H. Adler, a cardiologist at Stony Brook University Medical Center, has developed a VR training computer game for medical students called Heartworks. Heartworks allows students to differentiate between healthy and diseased heart structures and systems. This VR training provides students with a hands-on approach to understanding the complex cardiovascular system, making training fun and time-efficient. Dr. Adler notes that, unlike traditional methods of learning, VR training creates a classroom environment that allows students to experience and understand their ways of learning better.
Conclusion: VR has the potential to revolutionize medical training. It provides opportunities for medical professionals and students to practice complex medical procedures in a simulated environment that mimics real-life situations. This provides trainees with the opportunity to learn from their mistakes and better their skills without putting real patients at risk. The use of VR in medical education and training has been extensively researched by universities, organizations, and hospitals, and continues to hold promise for the future of healthcare.
12 Ways VR And AR Can Be Deployed In The Future – MobyGeek.com
Abstract: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technology holds a vast scope for application in various fields, from entertainment to education and healthcare. MobyGeek.com highlights 12 ways VR and AR technology can be deployed to improve healthcare, the most important being medical training in a risk-free environment.
Introduction: Virtual and Augmented Reality technologies have emerged as the key players in revolutionizing various aspects of human lives. These technologies have a vast scope of application in fields like entertainment, education, and healthcare. This technology provides a simulated experience by replicating an environment in 3D that mimics the real world.
Content: MobyGeek.com has outlined 12 ways VR and AR technology can be useful in healthcare. The most important and practical application of VR and AR technology in healthcare is providing medical training to medical professionals in a safe, risk-free virtual environment. The ability to practice medical procedures without any potential harm to patients can significantly increase the proficiency and skill set of medical professionals.
Another important application of VR and AR technology in healthcare is creating Mental health therapy programs. With the COVID-19 pandemic causing widespread social isolation and anxiety, the demand for mental healthcare services has increased. VR and AR can provide a convenient and private platform for mental healthcare therapy sessions. Patients can access virtual environments to recreate a sense of calm and relaxation during therapy sessions.
VR and AR technology can also aid in creating simulations for medical emergency situations training. Medical emergencies and disasters require quick thinking and action. However, it isn’t practical to train medical professionals under emergency circumstances. VR can create simulations to provide an experience in dealing with emergency medical situations such as mass casualty incidents or cardiac arrests. It provides a risk-free environment where medical professionals can efficiently learn the process of handling an emergency effectively.
VR technology can also improve patient care with the creation of virtual, interactive patient education programs. Patients can gain a better understanding of their medical conditions and will have more engagement in their treatment plans. VR can create interactive education sessions on complex medical procedures or surgeries, allowing patients to better understand the medical procedures they will undergo.
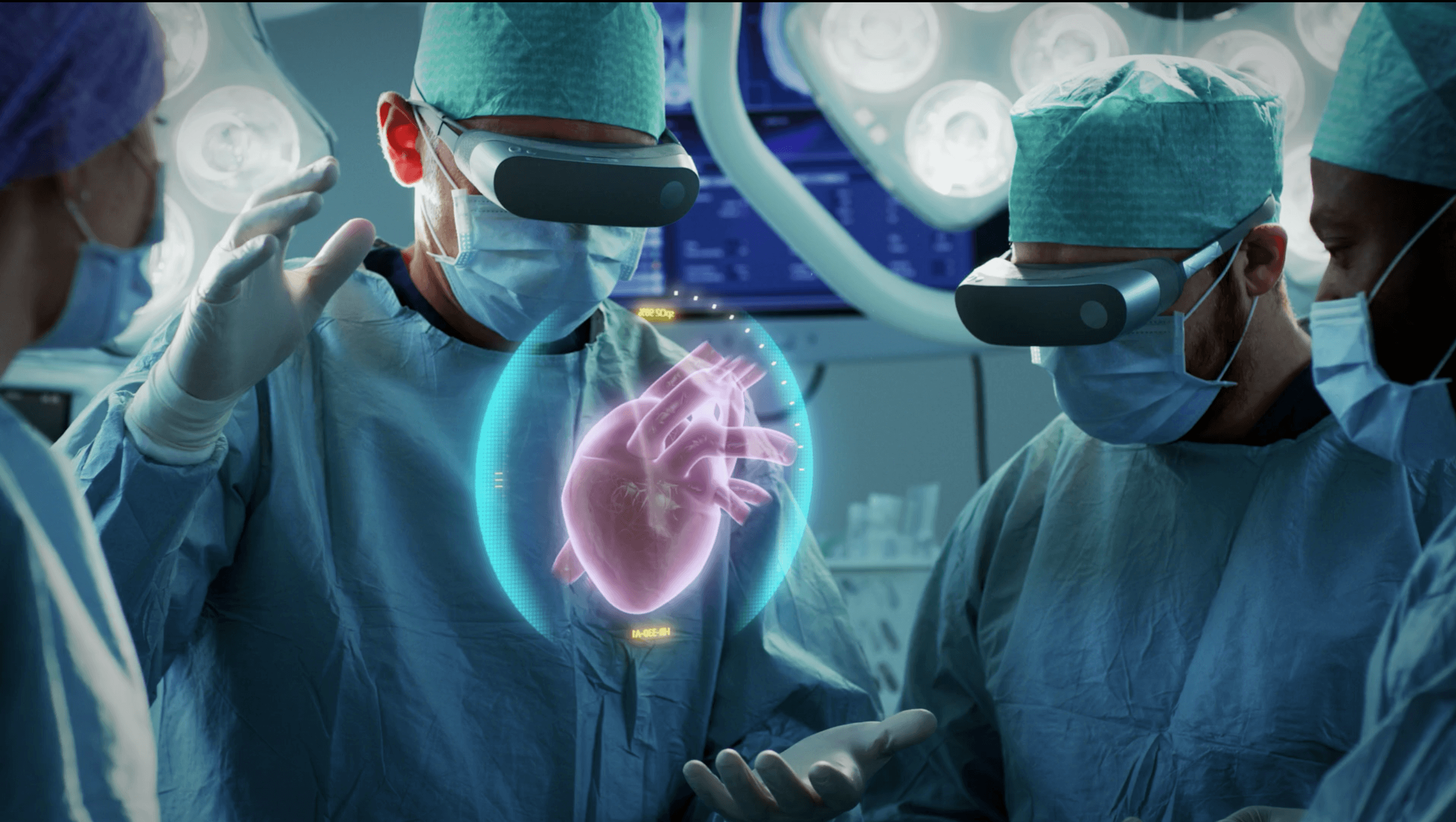
AR can provide additional support to medical professionals by creating a virtual reality representation of the patient’s anatomy. The technology allows doctors to view, in real-world practice, the internal anatomy of the human body, which helps provide a more accurate diagnosis and treatment of injuries or diseases.
While there is significant potential for VR and AR technology in healthcare, additional research must be carried out to optimize its use.
Conclusion: VR and AR technology can be a game-changer for healthcare by improving medical procedures, patient care, and medical training. The technology can provide medical professionals and students with a safe environment to practice procedures that mimic real-world scenarios. While there is a need for more research on this technology, the future of healthcare with the use of VR and AR is promising.
The Top 3 Healthcare Integrations Of VR And AR

Abstract: VR and AR have emerged as a valuable tool in healthcare, providing safe and risk-free experience for training medical professionals, diagnosing and treating patients, and creating a comprehensive educational experience. VR Fitness Insider highlights the top three healthcare integrations of VR and AR.
Introduction: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are becoming increasingly popular in healthcare. Physicians, researchers, and medical equipment manufacturers are making more extensive use of VR and AR to improve patient health, medical education, and clinical decision-making.
Content: VR and AR technology integration in healthcare provides virtual simulations of life-like scenarios for virtual medical training, surgical planning, and the creation of virtual autonomous avatars for patient health support. The top three healthcare integrations of VR and AR are:
- Virtual Reality in Medical Training: VR provides medical professionals with a safe and risk-free environment to practice surgical procedures, diagnosis of complicated diseases, and to stay current with the newest medical equipment
- AR-Assisted Surgical Planning: AR provides a comprehensive and accurate representation of the human anatomy in real-time during surgical procedures to identify any potential risks or anomalies before surgery is carried out.
- Virtual Autonomy for Patient Health Support: VR is being introduced in patient health support. These avatars are designed with customized features and personalities that enable patients to interact with them naturally for superior health support.
VR provides an immersive experience, allowing trainees to become involved in scenarios at their own pace. The VR can provide an opportunity for trainees to experience different levels of complexity to gain expertise in the field. The Medical Realities VR platform provides a comprehensive VR library containing different surgeries, allowing trainees to bring their surgical knowledge to a whole new level. VR dentistry offers dental students and dental professionals the opportunity to practice and examine realistic clinical scenarios involving dental procedures and related scientific materials.
AR is increasingly being introduced in hospitals to assist surgeons during critical surgeries to improve their decision-making abilities. AR overlays an accurate medical representation of the human anatomy in real-time over the patient’s body to provide a comprehensive and accurate surgical-view. The technology helps detect medical anomalies and precisely guides surgeons during complex surgical procedures.
The development of virtual autonomous avatars for patient health support with customized features keeps patients engaged in their treatment process, already gaining momentum in personalized medicine. These avatars are designed with life-like qualities to engage naturally with patients while providing essential feedback, monitoring vital signs and medication reminders, among other patient health support tasks.
Conclusion: VR and AR technology have revolutionized the healthcare industry, providing virtual training, accurate diagnosis, comprehensive surgical planning, and personalized medicine that transforms patients’ engagement and outcomes. The technology is user-friendly, provides an immersive experience to trainees to learn at their own pace, and helps support patients through virtual and life-like avatars. VR and AR technology promise to continue impacting the healthcare industry positively in the coming years.
Virtual Reality Medical Training: Another Healthcare Revolution?

Abstract: Medical training, a crucial aspect of quality healthcare, is time-consuming, expensive, and risk-prone for both patients and medical professionals. Virtual Reality (VR) Medical Training provides a safe and risk-free environment for medical professionals and students to practice medical procedures, and diagnose and treat diseases without putting patients at risk.
Introduction: Medical education and training require years of rigorous education and training to produce competent and proficient medical professionals. Traditional medical training methods are often expensive, time-consuming, and pose significant safety risks for medical professionals and patients. Lack of proper training and knowledge results in a significant number of malpractice suits, and operates on patient safety, which highlights the need for an effective and safe medical training method.
Content: Virtual Reality Medical Training provides medical students, residents, and practicing medical professionals with necessary medical surgical skills in a safe, risk-free environment. The ability to simulate realistic physical surgical scenarios and disease presentations provides medical students and residents with better opportunities for understanding and applying their learning. VR is efficient in training rare and challenging surgeries that are difficult to learn using traditional training methods.
Medical simulation training, with high-fidelity VR and other immersive technologies, has gained quality recognition, becoming a more effective alternative to shadowing or observing real surgeries. VR simulations provide students the freedom to explore medical scenarios in real-time, making mistakes in a safe space that doesn’t affect patients’ lives positively.
The value of VR simulation medical training is extending beyond surgical procedures, providing some of the most critical procedures of our time, such as intubation and medical emergency response training. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic created isolated training environments, where medical professionals must maintain social distancing protocols while receiving the necessary training. VR provides the solution by creating a safe and social distancing proof training environment. Medical professionals can experience and learn medical emergency procedures, treatment methods, and diagnosis through interactive training scenarios.
Another promising aspect of VR in healthcare is the ability to create accurate patient simulations. 3D patient scanning techniques have gained popularity in creating accurate body reproductions for simulation simulations. These simulations include tumor resections, streamlining of procedures, and medical testing without exposing patients to radiation or other dangers.
Conclusion: VR Medical training has emerged as the trendiest and most innovative solution to address the limitations of traditional medical training methods. The technology provides a practical solution to provide medical professionals with the necessary training, minimizing the risks to patients and trainees. The integration of VR technology in medical training curriculum is the next healthcare revolution, providing medical practitioners with the necessary skillsets to compete with the ever-growing complexity of healthcare procedures and medical infrastructure.

Source image : unimersiv.com
Source image : vstream.ie

Source image : mobygeek.com

Source image : www.vrfitnessinsider.com

Source image : touchstoneresearch.com




