New battery technology for renewable energy New battery tech

#image_title
Recent developments in battery technology for renewable energy have demonstrated the ability to enable rapid recharging of electric vehicles (EVs), potentially reducing the recharging time from hours to seconds.
Solid-state batteries, which employ a solid electrolyte rather than a liquid one, are a hopeful new technology. More energy can be kept in the same amount of room thanks to this. Additionally, solid-state batteries may charge more rapidly and last for longer than standard lithium-ion batteries.
Flow batteries, which employ a liquid medium and are therefore rechargable, are another promising technology. This innovation could be used to store energy generated from renewable sources like sun and wind, in addition to charging electric vehicles.
Graphene, a form of carbon that is both extremely thin and strong, is being used in batteries, and sodium-ion batteries, which are both cheaper and more ecologically friendly than conventional lithium-ion batteries, have also been developed.
The potential for renewable energy and electric mobility is exciting, even though these technologies are still in their infancy. Assuming they prove fruitful, they could facilitate the spread of renewable energy and lessen our dependence on fossil fuels.

Here are five new battery technologies that have the potential to change the world:
- Lithium-sulfur batteries: Lithium-sulfur batteries have a higher energy density than traditional lithium-ion batteries, which means they can store more energy in a smaller space. They are also cheaper to produce and more environmentally friendly.
- Zinc-air batteries: Zinc-air batteries use zinc and oxygen to generate electricity, which makes them a more sustainable alternative to lithium-ion batteries. They are also cheaper and more efficient, with the potential to last longer and store more energy.
- Solid-state batteries: Solid-state batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, which allows for a higher energy density and faster charging times. They are also safer and more stable than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
- Sodium-ion batteries: Sodium-ion batteries are a cheaper and more sustainable alternative to lithium-ion batteries. They use sodium instead of lithium, which is more abundant and less expensive, and they have the potential to last longer and store more energy.
- Organic flow batteries: Organic flow batteries use organic molecules to store and release energy, which makes them a more sustainable alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
They are also cheaper and easier to produce, with the potential to store more energy and last longer. These advances in battery technology may significantly improve our ability to hold and use energy in the future, leading to greater accessibility, efficiency, and sustainability. Although they are still in the research and development phase, they hold great promise for the future of renewable energy and electric vehicles.
How Much Wind Could A Wind Farm Farm? Web Tool Estimates Renewable
The amount of wind that a wind farm can generate relies on several factors, including the size and number of turbines, the wind speed and direction, and the location of the wind farm.
There are web tools accessible that can estimate the potential wind energy output of a wind farm based on these variables. One such tool is the Wind Integration National Dataset (WIND) Toolkit, which was created by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the United States.
The WIND Toolkit utilizes meteorological data to estimate the wind energy potential for specific locations in the United States. Users can enter the location of their wind farm, pick the turbine type and size, and examine the estimated wind energy output for various time periods, ranging from hourly to yearly averages.
Another web tool that assesses wind energy potential is the Global Wind Atlas, which was created by the Technical University of Denmark and the World Bank. This tool provides global wind resource data at a resolution of 1 km, enabling users to estimate the wind energy potential for specific locations around the globe.
These web tools can be helpful for developers and planners to estimate the potential wind energy output of a wind farm, which can inform choices about site selection, turbine size and number, and energy production estimates.

www.digitaltrends.com
renewable energy potential wind farm estimates tool web could much
New Battery Technology Could Help Unlock Solar, Wind Power Potential

www.atlanticrenewables.co.uk
By solving the problem of energy storage, advances in battery technology may allow solar and wind power to reach their maximum potential. It’s important to keep in mind that green energy sources like solar and wind can be unpredictable and thus not always used to meet demand. Given this, it may be challenging to depend solely on these resources for energy production.
With the advent of cutting-edge battery technology, however, we can now store the surplus energy produced by renewable sources like sun and wind and use it later. This has the potential to make renewable energy sources like solar and wind more reliable by mitigating the issue of intermittency.
Flow batteries, which have a liquid electrolyte that can be readily replaced, are a promising technology. Flow batteries can potentially store significant amounts of energy at low costs, making them a great option for storing surplus energy generated by renewables.
A further promising innovation is solid-state batteries, which employ a solid electrolyte rather than a watery one. Solid-state batteries are superior to conventional lithium-ion batteries in terms of energy density and charging speed, making them ideal for use in green energy storage infrastructure.
The use of sodium-ion batteries, which are both cheaper and less harmful to the environment than standard lithium-ion batteries, and the discovery of novel electrode materials have also contributed to the advancement of battery technology.
The overall potential of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power cannot be realized without the advancement of novel battery technology. These technologies can help us transition away from fossil fuels and into a more sustainable energy future by offering secure energy storage.
Renewable Energy: Getting To 100% Requires Cheap Energy Storage. But
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/64983110/shutterstock_1075034981.0.jpg)
www.vox.com
Transitioning to a more safe energy future relies heavily on renewable energy sources. But to get to 100% green energy, we need low-cost and high-efficiency energy storage options. Systems for storing energy can be used to keep renewable energy reserves for use when they are most required.
The cost of energy storage is still a major obstacle to achieving 100% renewable energy, despite the fact that there have been substantial advancements in energy storage technology. However, traditional lithium-ion batteries are currently the most widely used energy storage option, despite being both costly and limited in their lifespans.
To combat this problem, scientists are investigating a wide range of potential replacements for expensive and inefficient lithium-ion batteries. There are a number of alternatives to conventional batteries that have the ability to store more energy for less money.
The efficiency of renewable energy sources should be prioritized alongside the development of novel energy storage technologies. Technological improvements in wind turbines and solar panels, for instance, can increase the amount of energy produced from these sources, thereby reducing the amount of energy that must be stored.
Last but not least, legislation and regulation can play an important role in promoting the growth and widespread use of energy storage technologies. To better manage their renewable energy resources, governments can incentivize the development of new energy storage technologies and utilities can be urged to invest in energy storage systems.
In conclusion, while relying solely on renewable energy sources presents challenges, there are hopeful developments in energy storage technology, and the goal of a completely sustainable energy future is attainable with continued investment and policy support.
New Battery Tech ‘could Recharge EVs In Seconds, Not Hours

www.utilitycentre.co.uk
battery tech recharge seconds utilitycentre evs hours could
It would be a huge step forward for the electric vehicle business if there were a new battery technology that could recharge EVs in seconds instead of hours. Some consumers may be put off by electric cars because they require a faster and more reliable charging time than is currently available.
Supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries are the foundation of the novel battery technology currently under development. While lithium-ion batteries can store more energy for extended periods of time, supercapacitors can store and release large amounts of energy quickly. Researchers are hoping to create a battery with rapid charging and long-term storage by merging these two technologies.
Graphene-based electrodes are being considered as a means to boost the power production and energy density of supercapacitors. Solid-state batteries are also being investigated because of their potential to outperform lithium-ion batteries in terms of energy efficiency and charging time.
Potentially game-changing for the spread of EVs is a novel battery technology that has recently been developed. The convenience of EVs for long-distance travelers depends on the speed with which their batteries can be recharged. By reducing the time needed for charging and making EVs more convenient to use, faster charging times could also help to reduce the total cost of EV ownership.
It should be noted, however, that this technology is still in its early stages of development, and it could be several years before it is accessible to the general public. This is nonetheless a promising breakthrough in battery technology that may hasten the advent of a greener mode of transportation.
Renewable Energy, Bournemouth

www.fortunaworld.co.uk
Bournemouth, a coastal town in southern England, has a number of renewable energy options available for both residential and commercial customers. Some of the most common renewable energy options in Bournemouth include:
- Solar energy: Solar panels are a popular renewable energy option in Bournemouth, as the town receives a fair amount of sunlight throughout the year. By installing solar panels on rooftops or in open spaces, residents and businesses can generate their own electricity and reduce their reliance on the grid.
- Wind energy: Although not as popular as solar energy, wind energy can also be harnessed in Bournemouth. Small wind turbines can be installed on rooftops or in gardens to generate electricity, or larger wind farms can be developed offshore.
- Geothermal energy: While not as widely used in Bournemouth as other renewable energy options, geothermal energy can be harnessed using heat pumps that extract heat from the ground to provide heating and hot water for buildings.
- Hydro energy: As a coastal town, Bournemouth also has the potential to generate electricity using hydropower. This can be done through the use of tidal turbines or wave energy converters, which capture the energy of the waves to generate electricity.
Overall, there are a number of renewable energy options available in Bournemouth, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. The choice of which renewable energy option to pursue will depend on a number of factors, including the available resources, the size and location of the property, and the budget available. It is recommended to consult with a local renewable energy expert or installer to determine the most suitable renewable energy option for your specific needs.
energy renewable energies solar tax reform bill translation momentum earth slow could industry clean localization services bournemouth industries
Renewable Energy: What You Need To Know

taraenergy.com
energy renewable panels tara
Renewable energy is energy that is derived from natural resources that are replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat. It is considered an important alternative to non-renewable energy sources such as fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to climate change.
Here are some things you need to know about renewable energy:
- Types of renewable energy: There are several types of renewable energy, including solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages and can be harnessed in different ways.
- Benefits of renewable energy: Renewable energy has several benefits, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving energy security, and creating jobs. It can also reduce reliance on fossil fuels and help to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Challenges of renewable energy: Despite its benefits, renewable energy also faces several challenges. One of the biggest challenges is intermittency, as some renewable energy sources such as solar and wind are not always available. Other challenges include high upfront costs, the need for energy storage solutions, and resistance from traditional energy companies.
- Policy support: Governments around the world are implementing policies to support the growth of renewable energy, such as subsidies, tax incentives, and renewable energy targets. These policies can help to create a more favorable environment for renewable energy investment and deployment.
- Growth of renewable energy: The renewable energy industry has grown rapidly in recent years, with significant increases in installed capacity for solar and wind energy. In many parts of the world, renewable energy is now cost-competitive with traditional fossil fuels, and investment in renewable energy is expected to continue to grow in the coming years.
Overall, renewable energy is an important alternative to traditional fossil fuels and has the potential to play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
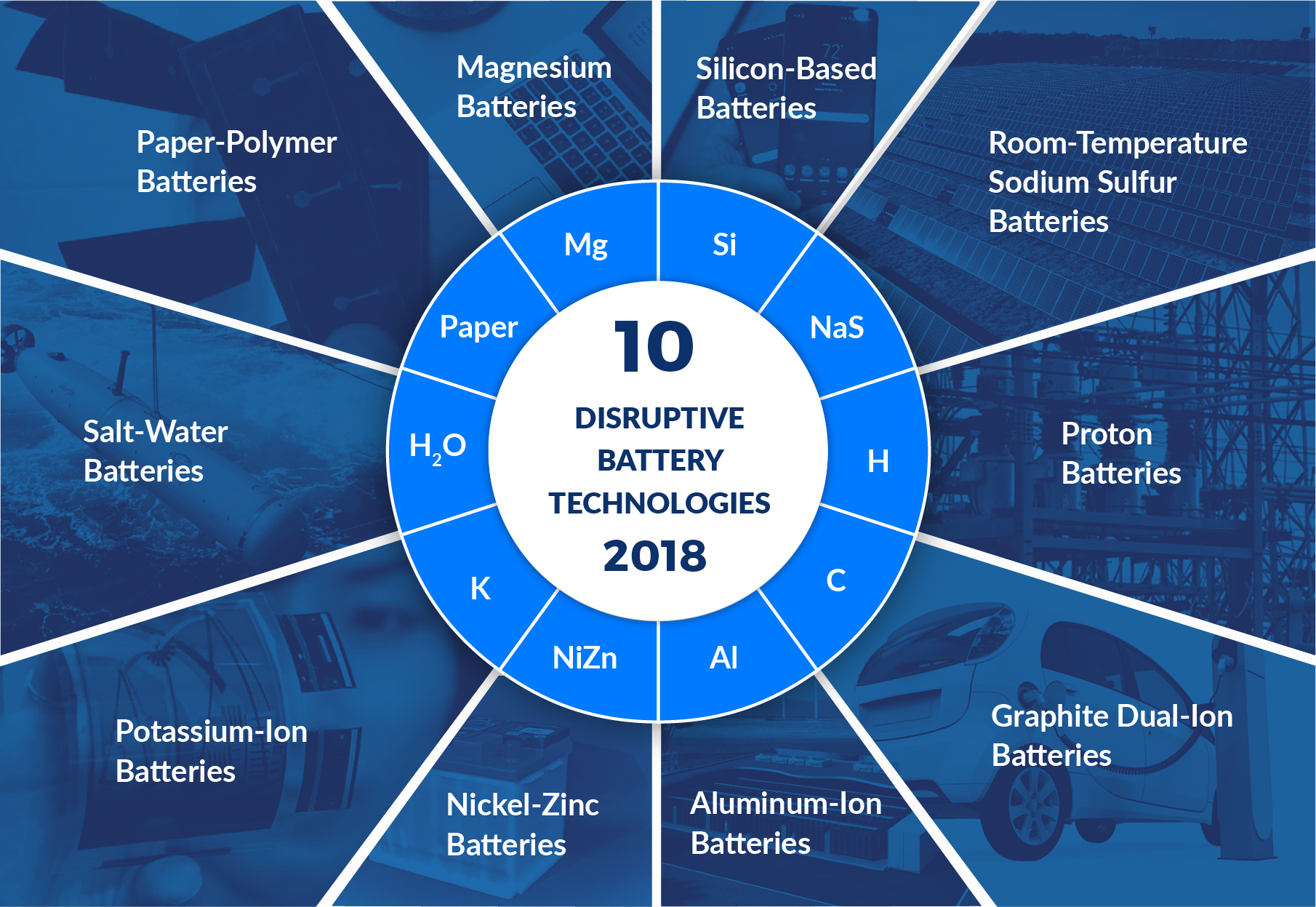
Best Batteries Technology In 2021
www.stocksmantra.in
batteries lithium vanadium investment nano uas
There are several battery technologies that are currently considered some of the best in 2021 due to their efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Here are some of the top battery technologies:
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries: Li-ion batteries are the most widely used battery technology due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and low self-discharge rate. They are used in a variety of applications, including electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy storage systems.
- Solid-state batteries: Solid-state batteries are a newer technology that use a solid electrolyte instead of the liquid electrolyte found in Li-ion batteries. They offer higher energy density and safety, as they are less prone to overheating and fires.
- Flow batteries: Flow batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that use two liquid electrolytes separated by a membrane to store energy. They are used in stationary energy storage applications, such as for renewable energy integration with the grid.
- Sodium-ion batteries: Sodium-ion batteries are a promising alternative to Li-ion batteries, as they use abundant and low-cost sodium instead of lithium. They offer comparable energy density and are more environmentally friendly.
- Zinc-air batteries: Zinc-air batteries use oxygen from the air as the cathode material, which makes them lightweight and low-cost. They have potential for use in electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Overall, Li-ion batteries are still the most widely used and best battery technology in terms of performance and reliability, but newer battery technologies such as solid-state, flow, sodium-ion, and zinc-air batteries show great promise for the future of energy storage.
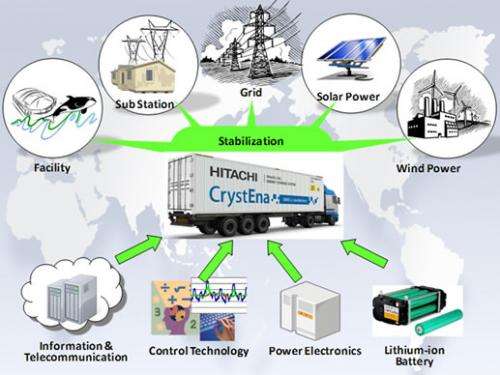
New Energy Storage System For Renewable Technologies
There are several new energy storage systems being developed and deployed to support renewable technologies such as solar and wind power. Here are a few examples:
- Lithium-ion batteries: Lithium-ion batteries are a popular choice for energy storage systems due to their high energy density and relatively low cost. They can be used in both residential and commercial applications to store energy generated from renewable sources.
- Flow batteries: Flow batteries use two liquid electrolytes separated by a membrane to store energy, offering high scalability and long cycle life. They are commonly used in large-scale energy storage systems, such as for wind and solar farms.
- Thermal energy storage: Thermal energy storage systems store excess heat generated from solar thermal systems or other sources in materials such as molten salt or concrete, which can be used to generate electricity when demand is high.
- Hydrogen fuel cells: Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen into electricity, with water as the only byproduct. They can be used in conjunction with renewable technologies to store excess energy and generate electricity when needed.
- Flywheels: Flywheels store kinetic energy in a rotating mass, allowing for quick and efficient energy storage and discharge. They are often used in commercial or industrial applications where high-power output is needed.
Overall, energy storage systems are critical for maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of renewable technologies. As the demand for renewable energy continues to grow, the development of new and innovative energy storage systems will play a key role in supporting the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
phys.org







