edge computing for autonomous driving opportunities and challenges
The Drive Towards Intelligent Edge Computing?
Abstract
Edge Computing is growing fast and has been identified as a key enabler of digital transformation. Intelligent Edge Computing is a new approach that is changing the way we think about computing infrastructure. In this article, we take a closer look at intelligent edge computing—what it is, how it differs from traditional edge computing, and why it’s important.
Introduction
Edge computing is quickly becoming a vital component of IT infrastructure due to the increasing demand for faster data processing and more agile operations. The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G networks, and cloud computing has accelerated the adoption of edge computing. Intelligent edge computing is the next step in this evolution.
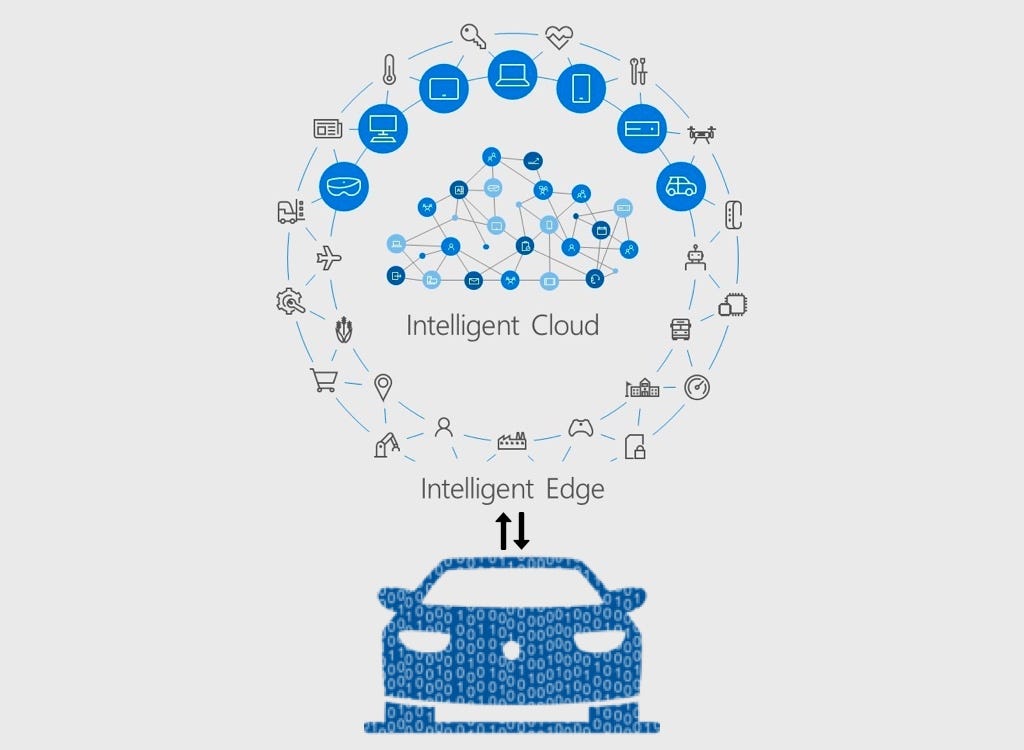
Intelligent edge computing is the practice of processing data near the source of data generation or the edge of the network, using machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze and react to that data in real-time. By processing the data closer to the source, organizations can reduce latency, improve response times, and free up network bandwidth.
Traditional edge computing involves processing data at the edge of the network before transmitting it to the cloud or data center for further analysis. This approach is effective, but it has its limitations. For example, it doesn’t allow for real-time processing of large amounts of data, which is a critical requirement for many organizations today.
Intelligent edge computing takes traditional edge computing to the next level by incorporating machine learning and artificial intelligence into the process. This means that the edge device can analyze the data it has collected and make decisions based on that analysis. For example, if an IoT sensor detects a spike in temperature, it can automatically adjust the cooling system to prevent equipment damage. This real-time decision-making is crucial for many organizations, especially those that operate in high-risk environments.
Content
Intelligent Edge Computing offers several advantages over traditional edge computing. Here are a few:
Real-Time Decision Making
Intelligent edge computing enables real-time decision-making at the edge of the network. This means that organizations can respond to events as they happen, without needing to wait for data to be transmitted to the cloud or data center. This is particularly important in applications where time is of the essence, such as in autonomous vehicles, manufacturing plants, and healthcare settings.
Improved Network Traffic
By processing data at the edge of the network, organizations can reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud or data center. This can help reduce network congestion and improve overall network performance. This is particularly important for organizations that operate in remote or bandwidth-constrained environments.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
By processing data at the edge of the network, organizations can reduce their reliance on cloud or data center resources. This can help lower costs and improve efficiency. Additionally, by incorporating machine learning and artificial intelligence into the processing pipeline, edge devices can make intelligent decisions on their own, without needing to rely on human intervention.
Flexibility and Scalability
Intelligent edge computing offers organizations greater flexibility and scalability than traditional edge computing. By incorporating machine learning and artificial intelligence into the process, organizations can adapt to changing conditions in real-time. This means that edge devices can adjust their processing requirements based on changing workloads or resource constraints.
While intelligent edge computing offers many advantages, it is not without its challenges. Here are a few:
Data Security and Privacy
Processing data at the edge of the network can create new security and privacy risks. Edge devices are often more vulnerable to attacks than cloud or data center resources. Additionally, processing sensitive data at the edge of the network could lead to data leaks or breaches. Organizations must take steps to secure their edge devices and data to mitigate these risks.
Data Governance and Management
Intelligent edge computing creates new challenges for data governance and management. With data being processed and analyzed at the edge of the network, organizations must ensure that their data is accurate, consistent, and up-to-date. This requires new approaches to data governance and management.
Data Volume and Complexity
Intelligent edge computing generates large amounts of data, which can be overwhelming for organizations to manage. Additionally, the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms can add complexity to the processing pipeline, which can be difficult for some organizations to manage.
Despite these challenges, intelligent edge computing is gaining traction among organizations that want to leverage the advantages it offers. Here are a few use cases:
Healthcare
Intelligent edge computing can be used in healthcare settings to monitor patients in real-time. For example, wearable devices can track a patient’s vital signs and alert healthcare providers if there is a need for intervention. Additionally, edge devices can be used to monitor hospital equipment and alert maintenance personnel if there is a problem.
Manufacturing
Intelligent edge computing can be used in manufacturing settings to monitor equipment in real-time. For example, sensors can detect when a piece of equipment is performing poorly and automatically schedule maintenance before it fails. Additionally, edge devices can be used to monitor the quality of products as they are being manufactured.
Transportation
Intelligent edge computing can be used in transportation settings to monitor vehicles in real-time. For example, sensors can detect when components of a vehicle require maintenance or repair, reducing the risk of equipment failure. Additionally, edge devices can be used to monitor traffic conditions in real-time, enabling drivers to adjust their routes to avoid traffic congestion.
Smart Cities
Intelligent edge computing can be used in smart city applications to monitor environmental conditions in real-time. For example, sensors can detect changes in air quality and alert city officials if there is a need for intervention. Additionally, edge devices can be used to manage traffic flow and parking, reducing congestion and improving the overall quality of life in cities.
Conclusion
Intelligent edge computing is a new approach that is changing the way we think about computing infrastructure. By processing data at the edge of the network using machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms, organizations can improve response times, reduce network congestion, and make real-time decisions. While there are challenges associated with intelligent edge computing, its advantages make it a compelling option for many organizations.
Motivation, Challenges and Opportunities in Edge Computing

Abstract
Edge computing has been gaining traction as more and more organizations look to improve their digital transformation outcomes. In this article, we explore the motivations, challenges, and opportunities of edge computing.
Introduction
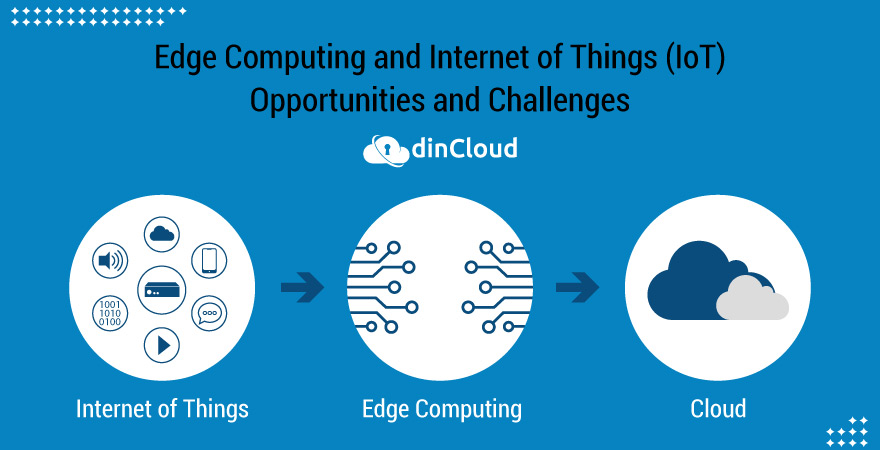
Edge computing is an emerging technology that is gaining momentum due to the increasing demand for faster and more responsive computing capabilities. Edge computing involves processing data at the edge of the network, often on devices like IoT sensors, before transmitting it to the cloud or data center for further analysis.
The growth of edge computing has been driven by several factors, including the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), the need for low latency, and the increasing demand for real-time data processing capabilities. In this article, we take a closer look at the motivations, challenges, and opportunities of edge computing.
Content
Motivations
Edge computing is motivated by several key factors:
Low Latency
One of the key motivations for edge computing is the need for low latency. In many applications, such as autonomous vehicles or manufacturing plants, response times must be measured in milliseconds. By processing data at the edge of the network, organizations can reduce latency and improve response times.
Real-Time Data Processing
Another motivation for edge computing is the need for real-time data processing capabilities. In many applications, like financial trading or healthcare, data must be processed in real-time to be effective. By processing data at the edge of the network, organizations can make real-time decisions based on that data.
Data Privacy and Security
Edge computing can also be motivated by a desire to ensure data privacy and security. By processing data locally, organizations can avoid transmitting sensitive data over public networks. Additionally, by limiting access to devices at the edge of the network, organizations can reduce the risk of a cyber-attack.
Challenges
Edge computing is not without its challenges:
Security
Security is a critical challenge for edge computing. Edge devices are often more vulnerable to attacks than cloud or data center resources. Additionally, processing sensitive data at the edge of the network could lead to data leaks or breaches. Organizations must take steps to secure their edge devices and data to mitigate these risks.
Data Governance and Management
Edge computing creates new challenges for data governance and management. With data being processed and analyzed at the edge of the network, organizations must ensure that their data is accurate, consistent, and up-to-date. This requires new approaches to data governance and management.
Data Volume and Complexity
Edge computing generates large amounts of data, which can be overwhelming for organizations to manage. Additionally, the complexity of the processing pipeline can be difficult for organizations to manage.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, edge computing offers several opportunities:
Improved Data Processing
Edge computing enables organizations to process data faster and more efficiently. By processing data at the edge of the network, organizations can reduce latency and improve response times. Additionally, with the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms, edge devices can analyze data in real-time and make intelligent decisions based on that analysis.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
Edge computing can help organizations lower costs and improve efficiency. By processing data at the edge of the network, organizations can reduce their reliance on cloud or data center resources. Additionally, with the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms, edge devices can make intelligent decisions on their own, reducing the need for human intervention.
Increased Flexibility and Scalability
Edge computing offers organizations greater flexibility and scalability than traditional computing methods. With the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence, edge devices can adapt to changing conditions in real-time. This means that edge devices can adjust their processing requirements based on changing workloads or resource constraints.
Conclusion
Edge computing is an emerging technology that is gaining momentum due to the increasing demand for faster and more responsive computing capabilities. By processing data at the edge of the network, organizations can reduce latency, improve response times, and make real-time decisions. While there are challenges associated with edge computing, its advantages make it a compelling option for many organizations.

Source image : medium.com
Source image : www.dincloud.com

Source image : www.researchgate.net


