edge computing definition and examples
As technology continues to advance, new innovations emerge that disrupt traditional ways of doing things. Edge computing is one of these innovations that have the potential to revolutionize financial services.
Edge Computing in Financial Services

Abstract
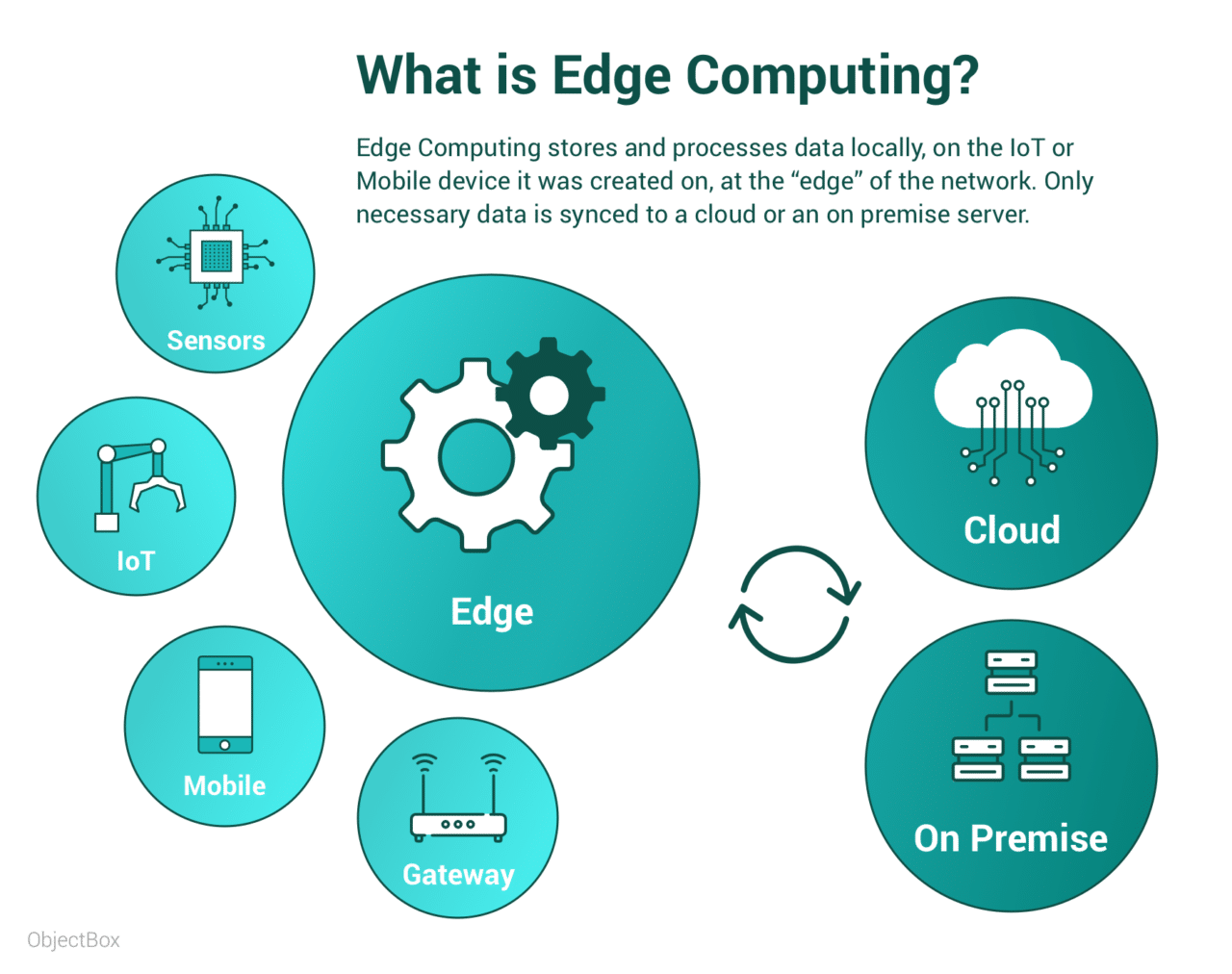
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed to improve response time and save bandwidth. With edge computing, data is processed and analyzed locally, which reduces the latency associated with sending data to the cloud for processing.
In the financial services industry, edge computing is gaining traction due to its ability to process large amounts of data in real-time, which is essential for mission-critical applications such as fraud detection, cybersecurity, and trading.
Introduction
With edge computing, data is processed at the edge of the network, near the devices or sensors that generate it. This means that edge devices, such as smartphones, sensors, and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices, can process data in real-time, without having to send it to the cloud, where it would have to go through multiple layers of infrastructure before being processed.
This greatly reduces response time and saves bandwidth, making it ideal for industries that require real-time processing, such as financial services. Edge computing enables financial institutions to process data in real-time, which is essential for applications such as fraud detection, cybersecurity, and trading.
Edge Computing Use Cases in Financial Services
Edge computing has several use cases in financial services, including:
- Fraud Detection: Fraud detection is a critical function in financial services that requires real-time data processing. With edge computing, fraud detection algorithms can be deployed at the edge of the network, where they can process data in real-time and detect fraud before it occurs.
- Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity is another area where edge computing can be beneficial. With edge computing, security algorithms can be deployed at the edge of the network, where they can monitor and detect potential threats in real-time.
- Trading: Trading requires real-time access to data and analysis, which can be challenging with traditional cloud-based computing. With edge computing, trading algorithms can be deployed at the edge of the network, where they can process data in real-time and make trades based on real-time market conditions.
Benefits of Edge Computing in Financial Services
Edge computing offers several benefits for financial services, including:
- Real-Time Data Processing: Edge computing enables real-time data processing, which is essential for mission-critical applications such as fraud detection, cybersecurity, and trading.
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing reduces latency by processing data locally, which improves response time and saves bandwidth.
- Increased Security: Edge computing enhances security by processing data locally, which reduces the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
Challenges of Edge Computing in Financial Services
While edge computing offers several benefits for financial services, it also comes with its challenges, including:
- Cost: Edge computing requires a significant investment in infrastructure, which can be costly for financial institutions.
- Complexity: Edge computing is a complex technology that requires specialized skills and expertise to deploy and manage.
- Integration: Integrating edge computing with legacy systems can be challenging, as it requires careful planning and coordination.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a disruptive technology that has the potential to revolutionize financial services. With its ability to process data in real-time, reduce latency, and enhance security, it is no surprise that financial institutions are exploring its use for mission-critical applications such as fraud detection, cybersecurity, and trading.
While edge computing comes with its challenges, such as cost, complexity, and integration, financial institutions that can successfully deploy and manage the technology will reap the benefits of increased efficiency, improved security, and real-time data processing.

Source image : www.deltecbank.com

Source image : objectbox.io

Source image : nicolaswindpassinger.com


