edge computing defined

So have y’all heard bout Edge Computing? Let’s get into it.
Edge Computing: ¿En qué consiste y cuáles son sus aplicaciones?

First off, let me break it down for ya! Edge Computing is a new way of processing data that takes place closer to the source of the data. Traditionally, data from devices is sent to a cloud-based server for processing, but with Edge Computing, the processing of that data happens on the device itself or on a local server.
So what does that mean for us? Well, it means faster processing times and less reliance on cloud-based servers. Plus, it can save us money in the long run because we won’t have to pay for as much cloud storage.
But what are some practical applications of Edge Computing? One example is in the world of self-driving cars. With the vast amounts of data being generated by self-driving cars, it would be impractical to send all that data to a cloud-based server for processing. By using Edge Computing, the data can be processed more quickly and efficiently while still maintaining the safety of the passengers.
Edge-Computing | Erklärung und Definition – IONOS
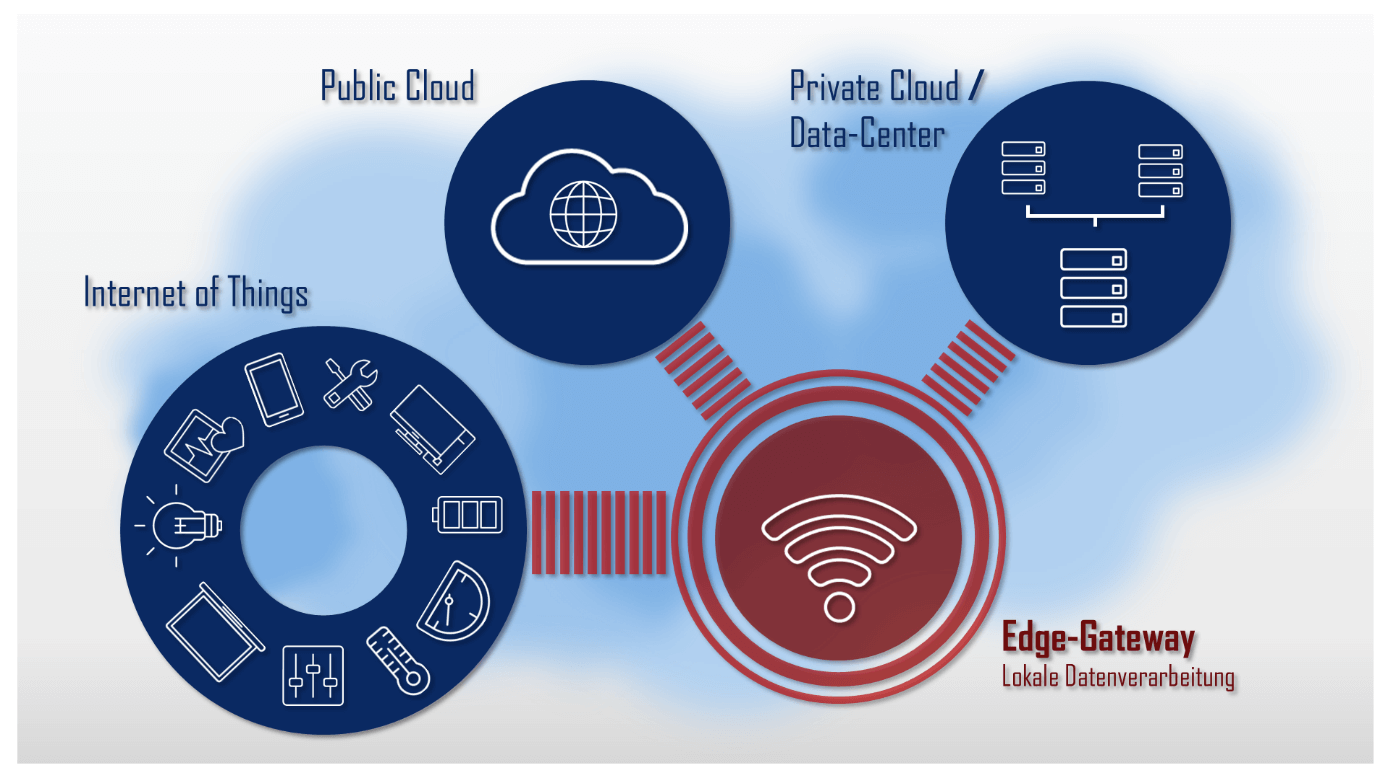
Now, let’s take a closer look at the definition of Edge Computing. Essentially, Edge Computing is a decentralized approach to computing that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, i.e. the edge of the network.
Nowadays, we are generating more data than ever before, and with the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), we are seeing an explosion in the number of devices producing that data. Edge Computing allows us to process that data more efficiently and effectively by reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud for processing.
Abstract
Edge Computing is a new approach to computing that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed. It has a wide range of practical applications, ranging from self-driving cars to the Internet of Things. By processing data at the edge of the network, we can reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud for processing, leading to faster and more efficient processing times.
Introduction
When it comes to computing, we are constantly looking for ways to make things faster, more efficient, and cheaper. Edge Computing is one of the latest trends in the world of computing, promising to revolutionize the way we process data.
In this article, we will take a closer look at what Edge Computing is, how it works, and what its practical applications are. We will explore the benefits of Edge Computing and discuss some of the potential drawbacks. We will also look at some of the key players in the world of Edge Computing and examine their role in shaping the future of computing.
Content
How Edge Computing Works
At its core, Edge Computing is all about bringing computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed. Traditionally, data is sent from devices to a cloud-based server for processing, but with Edge Computing, the processing happens on the device itself or on a local server.
Why is this important? Well, it means that we can process data more quickly and efficiently. When data is sent to a cloud-based server, it has to travel over the internet, which can take time depending on the size of the data and the speed of the internet connection. By processing the data at the edge of the network, we can reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent over the internet, leading to faster processing times.
Another advantage of Edge Computing is that it reduces our reliance on cloud-based servers. While cloud-based servers are a great way to store and process large amounts of data, they can be expensive to use, and there are always concerns about security and privacy. By using Edge Computing, we can reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud, potentially saving us money in the long run.
Practical Applications of Edge Computing
So what are some of the practical applications of Edge Computing? Let’s take a closer look:
1. Self-Driving Cars
Self-driving cars are one of the most exciting applications of Edge Computing. These vehicles generate vast amounts of data as they drive around, including data on their surroundings, their speed, and their position on the road. Traditionally, this data would be sent to a cloud-based server for processing, but with Edge Computing, the processing can happen in real-time on board the vehicle. This leads to faster and more efficient processing times, which is essential for the safety of the passengers.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly growing area of technology that involves the interconnection of devices over the internet. Examples of IoT devices include smart home devices, wearables, and industrial sensors. With so many devices connected to the internet, the amount of data being generated is staggering. Edge Computing allows us to process that data more efficiently by bringing computation and data storage closer to the devices themselves. This can lead to faster and more efficient processing times, which is essential for many IoT applications.
3. Healthcare
In the world of healthcare, Edge Computing has a wide variety of applications. For example, wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers generate a vast amount of data on the health and wellbeing of the wearer. By using Edge Computing, this data can be processed more quickly and efficiently, allowing healthcare professionals to make more informed decisions about the care of their patients.
Benefits of Edge Computing
There are many benefits to using Edge Computing in your business or organization. Here are just a few:
1. Faster processing times
By processing data at the edge of the network, we can reduce the amount of time it takes to process that data. This leads to faster processing times and more efficient use of resources.
2. Reduced reliance on cloud-based servers
Cloud-based servers are a great way to store and process large amounts of data, but they can be expensive and there are always concerns about security and privacy. By using Edge Computing, we can reduce our reliance on cloud-based servers and keep more of our data local.
3. Better data privacy and security
With Edge Computing, data is processed locally rather than being sent to a cloud-based server. This can help to improve data privacy and security, as there is less risk of data being intercepted or hacked during transit.
Potential Drawbacks
While there are many benefits to using Edge Computing, there are also some potential drawbacks. Here are a few to keep in mind:
1. Increased complexity
Edge Computing is a new and complex technology, which means that it may take some time for businesses and organizations to get up to speed with it.
2. Compatibility issues
Because Edge Computing relies on local processing rather than cloud-based processing, there may be compatibility issues with existing hardware and software. This can lead to additional costs and time spent on troubleshooting.
3. Data management challenges
With Edge Computing, data is processed locally, which means that businesses and organizations will need to develop new systems and processes for managing that data. This can be a major challenge, especially for organizations with large amounts of data.
Key Players in the World of Edge Computing
There are a number of companies and organizations that are leading the way when it comes to Edge Computing. Here are a few of the key players to keep an eye on:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is the leading provider of cloud-based services, and they are also making a big push into the world of Edge Computing. Their AWS Greengrass service is designed to help businesses and organizations deploy Edge Computing solutions quickly and efficiently.
2. Microsoft
Microsoft is another major player in the world of Edge Computing. They offer a range of tools and services for developing Edge Computing solutions, including their Azure IoT Edge service.
3. Intel
Intel is a leader in the world of CPUs and processors, and they are also heavily involved in the world of Edge Computing. Their OpenVINO toolkit is designed to help businesses and organizations develop Edge Computing solutions that can run on a wide range of hardware platforms.
Conclusion
Edge Computing is a new and exciting technology that promises to revolutionize the way we process data. By bringing computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, we can process data more quickly and efficiently, leading to faster processing times and more efficient use of resources.
While there are some potential drawbacks to using Edge Computing, such as increased complexity and compatibility issues, the benefits outweigh the risks for many businesses and organizations. As more companies and organizations begin to adopt Edge Computing, we can expect to see even more exciting applications of this technology in the years to come.

Source image : www.insightsonindia.com

Source image : edgecomputing.cl

Source image : www.ionos.at


