edge computing blockchain

#image_title
Blockchain-based secure storage and edge computing resource markets for mobile blockchain are two important aspects of modern technology that are changing the way we think about data management and storage. In this article, we’ll explore these topics in greater detail, examining the current state of play and the potential impact on industries ranging from finance and healthcare to manufacturing and logistics.
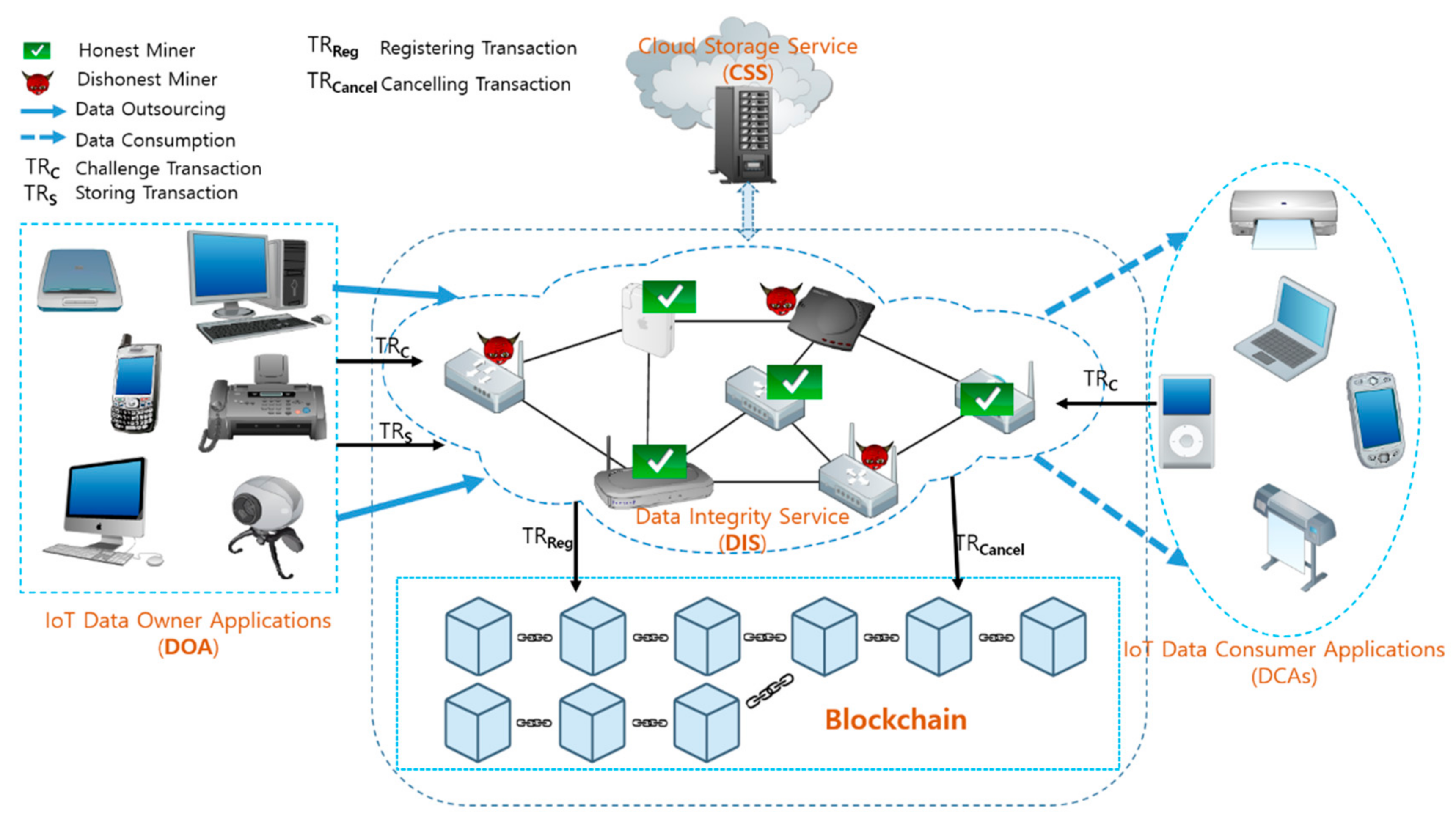
Blockchain-Based Secure Storage
Blockchain technology is primarily associated with cryptocurrency, but it has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of applications beyond finance. One area that is particularly exciting is secure storage. The basic principle of blockchain-based secure storage is that instead of relying on a single, centralized database that is vulnerable to hacking or data loss, data is distributed across a network of nodes, each of which has a copy of the data.
This makes it much more difficult for hackers to gain access to sensitive information, since they would have to simultaneously compromise a significant number of nodes to gather useful data. Additionally, because data is stored in a decentralized fashion, it is much more resistant to attacks that would seek to take down a single database or server, since there is no single point of failure.
While the idea of distributed storage is not new (think of peer-to-peer file sharing networks), blockchain storage takes this concept to the next level by adding elements of security and accountability. Most implementations of blockchain-based storage use permissions to control access to sensitive data. By requiring cryptographic proof that a user is authorized to access specific data, it becomes much harder for unauthorized users to access critical information.
Example: Blockchain-Based Electronic Health Records
One area where blockchain-based secure storage is already being implemented in a significant way is in the realm of electronic health records (EHRs). EHRs are a critical component of modern healthcare, allowing doctors and other healthcare professionals to easily access patient information and coordinate care.
However, the centralized nature of most EHR systems makes them vulnerable to data breaches and cyber attacks. By storing EHRs on a blockchain, healthcare organizations can improve security by distributing the data across the network and controlling access through cryptographic keys. Additionally, because blockchain storage is inherently tamper-proof, organizations can be confident that patient data has not been altered or modified without proper authorization.
The potential benefits of blockchain-based EHRs go beyond simple security considerations, however. By using a distributed system, EHRs become much more flexible and interoperable, allowing for easier sharing of patient data across different healthcare organizations and systems. This could significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs by enabling more efficient and effective care coordination.
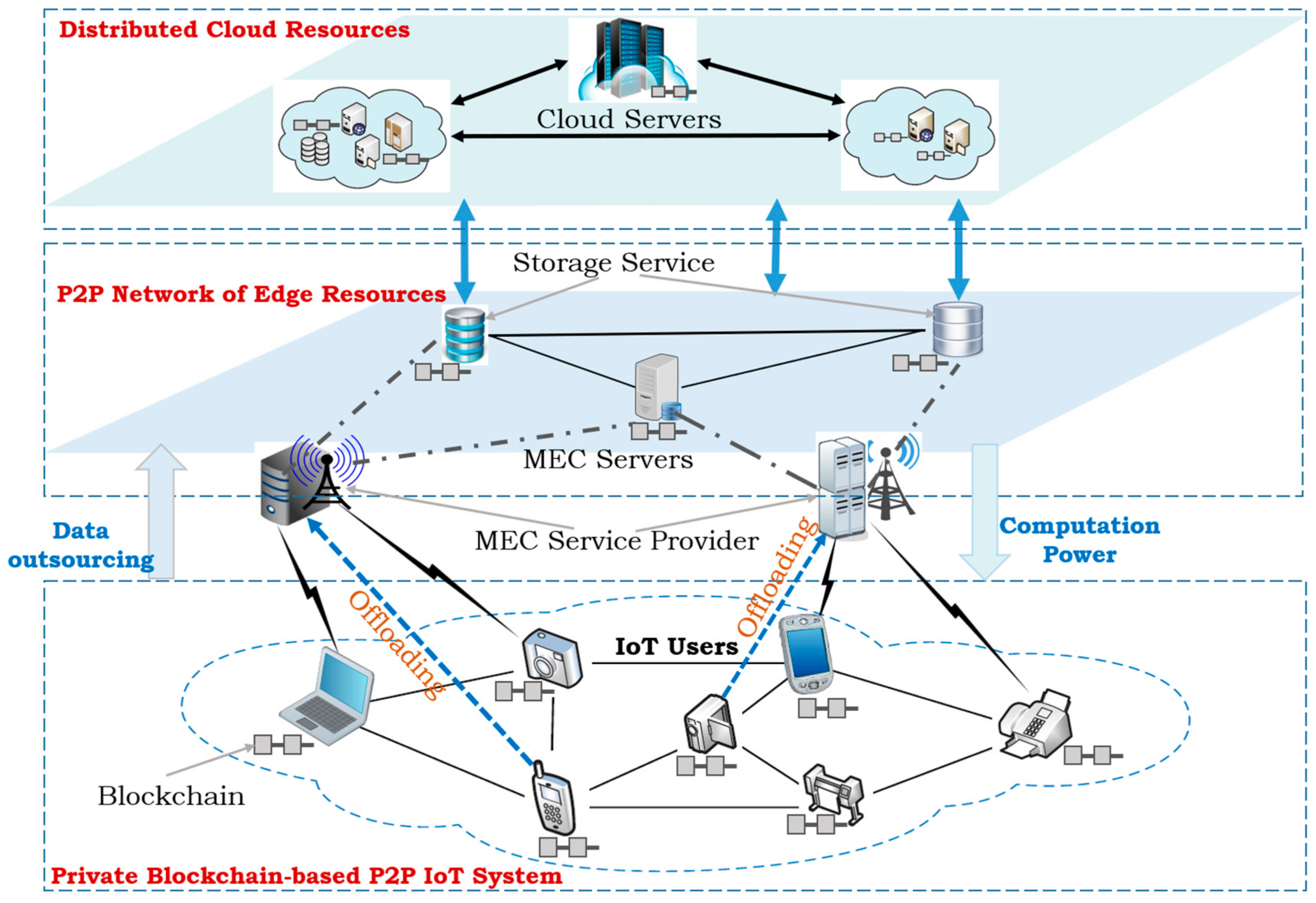
Edge Computing Resource Market for Mobile Blockchain
As more and more applications move to the cloud, there is increasing interest in edge computing as a way to reduce latency, improve scalability, and provide greater control over data. Edge computing, broadly defined, refers to the practice of processing data closer to where it is generated, rather than sending it to a centralized data center for processing.
Mobile blockchain represents a particularly interesting use case for edge computing. Mobile devices are inherently mobile (hence the name), and often generate large amounts of data that need to be processed in real-time. By using edge computing resources, mobile blockchain applications can improve performance and reliability by offloading some of the processing burden from the mobile device to the edge.
The term “edge computing resource market” refers to the ecosystem of resources that are available for developers to leverage as they build and deploy edge computing applications. These resources can include edge computing platforms (such as AWS IoT Greengrass), devices (such as Raspberry Pi), and even crowdsourced resources (such as SETI@home).
Example: Mobile Blockchain-Based Supply Chain Management
One area where mobile blockchain and edge computing are particularly well-suited is supply chain management. By using sensors and other IoT technologies to track goods as they move through the supply chain, organizations can gain greater visibility into the status and location of their shipments.
This data can then be stored on a blockchain, providing a tamper-proof record of the journey that the goods have taken. However, processing all of this data in real-time can be challenging, particularly on resource-constrained mobile devices.
By leveraging edge computing resources, such as those provided by AWS IoT Greengrass, organizations can offload some of the processing burden to the edge, reducing latency and improving reliability. Additionally, by using a distributed network of edge resources, it may be possible to process data more efficiently and cost-effectively than would be possible with a centralized data center.
Abstract
Blockchain-based secure storage and edge computing resource markets for mobile blockchain are two important areas of technology that are changing the way we think about data storage and management. By using a distributed, tamper-proof system for data storage and processing data closer to where it is generated, organizations can significantly improve security, scalability, and efficiency for a wide range of applications.
Introduction
With the rise of cloud computing and IoT technologies, there is more interest than ever in new approaches to data storage and processing. Two areas that are proving particularly exciting are blockchain-based secure storage and edge computing resource markets for mobile blockchain.
Blockchain-based secure storage provides a distributed, tamper-proof system for storing sensitive data, increasing security and reducing the risk of data breaches. Edge computing, on the other hand, involves processing data closer to where it is generated, reducing latency and improving reliability for resource-constrained mobile devices.
Both of these technologies have significant potential to transform a wide range of industries, from finance and healthcare to manufacturing and logistics. In the following sections, we’ll explore each of these topics in detail, looking at real-world examples of how they are being used today and the potential benefits they offer.
Blockchain-Based Secure Storage
Blockchain technology, which was first popularized by Bitcoin, has found numerous applications beyond finance. One area where it is proving particularly useful is in secure data storage. Traditionally, data has been stored in centralized databases, which are vulnerable to hacking and data breaches. By using a distributed, tamper-proof system for data storage, organizations can significantly improve security and reduce the risk of costly data breaches.
How Blockchain-Based Secure Storage Works
At its core, blockchain-based secure storage works by storing data on a distributed network of nodes, rather than in a centralized database. Each node has a copy of the data, and changes to the data are made through a consensus mechanism that ensures that all nodes on the network agree on the current state of the data.
Because each node has a copy of the data, it is much more difficult for hackers to gain access to sensitive information. Additionally, because data is stored in a decentralized fashion, it is much more resistant to attacks that would seek to take down a single database or server, since there is no single point of failure.
Most implementations of blockchain-based secure storage also use permissions to control access to sensitive data. By requiring cryptographic proof that a user is authorized to access specific data, it becomes much harder for unauthorized users to access critical information.
Example: Blockchain-Based Electronic Health Records
One area where blockchain-based secure storage is already being implemented in a significant way is in the realm of electronic health records (EHRs). EHRs are a critical component of modern healthcare, allowing doctors and other healthcare professionals to easily access patient information and coordinate care. However, the centralized nature of most EHR systems makes them vulnerable to data breaches and cyber attacks.
By storing EHRs on a blockchain, healthcare organizations can improve security by distributing the data across the network and controlling access through cryptographic keys. Additionally, because blockchain storage is inherently tamper-proof, organizations can be confident that patient data has not been altered or modified without proper authorization.
The potential benefits of blockchain-based EHRs go beyond simple security considerations, however. By using a distributed system, EHRs become much more flexible and interoperable, allowing for easier sharing of patient data across different healthcare organizations and systems. This could significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs by enabling more efficient and effective care coordination.
Conclusion: The Future of Blockchain-Based Secure Storage
Blockchain-based secure storage is an exciting new technology that has the potential to revolutionize data storage and management. By using a distributed, tamper-proof system for data storage and control, organizations can significantly improve security and reduce the risk of costly data breaches. Additionally, by using permissions to control access to sensitive data, it becomes much harder for unauthorized users to gain access to critical information.
As blockchain-based secure storage continues to evolve, it will likely find applications in a growing number of industries beyond healthcare. For example, finance organizations may use blockchain-based storage to improve the security of sensitive financial data, while logistics companies may use it to track and manage shipments more efficiently.
Edge Computing Resource Market for Mobile Blockchain
As more and more applications move to the cloud, there is increasing interest in edge computing as a way to reduce latency, improve scalability, and provide greater control over data. Edge computing, broadly defined, refers to the practice of processing data closer to where it is generated, rather than sending it to a centralized data center for processing.
Mobile blockchain represents a particularly interesting use case for edge computing. Mobile devices are inherently mobile (hence the name), and often generate large amounts of data that need to be processed in real-time. By using edge computing resources, mobile blockchain applications can improve performance and reliability by offloading some of the processing burden from the mobile device to the edge.
The term “edge computing resource market” refers to the ecosystem of resources that are available for developers to leverage as they build and deploy edge computing applications. These resources can include edge computing platforms (such as AWS IoT Greengrass), devices (such as Raspberry Pi), and even crowdsourced resources (such as SETI@home).
Example: Mobile Blockchain-Based Supply Chain Management
One area where mobile blockchain and edge computing are particularly well-suited is supply chain management. By using sensors and other IoT technologies to track goods as they move through the supply chain, organizations can gain greater visibility into the status and location of their shipments.
This data can then be stored on a blockchain, providing a tamper-proof record of the journey that the goods have taken. However, processing all of this data in real-time can be challenging, particularly on resource-constrained mobile devices.
By leveraging edge computing resources, such as those provided by AWS IoT Greengrass, organizations can offload some of the processing burden to the edge, reducing latency and improving reliability. Additionally, by using a distributed network of edge resources, it may be possible to process data more efficiently and cost-effectively than would be possible with a centralized data center.
Conclusion: The Future of Edge Computing Resource Markets for Mobile Blockchain
Edge computing resource markets for mobile blockchain represent an exciting new frontier for developers and organizations looking to build robust, reliable, and scalable mobile blockchain applications. By leveraging the power of edge computing, it is possible to significantly improve the performance and reliability of mobile blockchain applications, while also reducing the cost and complexity of deploying and managing these applications.
As the edge computing resource market continues to evolve, we can expect to see an ever-growing ecosystem of resources and tools for developers to leverage. These resources will likely include a mix of edge computing platforms, devices, and crowdsourced resources, creating a vibrant and dynamic ecosystem that will drive innovation and growth in the mobile blockchain space.
Conclusion
Blockchain-based secure storage and edge computing resource markets for mobile blockchain represent two exciting new frontiers in the world of data storage and processing. By using a distributed, tamper-proof system for data storage and processing data closer to where it is generated, organizations can significantly improve security, scalability, and efficiency for a wide range of applications.
As these technologies continue to evolve and mature, we can expect to see them deployed in an increasingly diverse range of industries and applications, driving innovation and growth across the technology landscape. Whether you are a developer looking to build innovative new mobile blockchain applications, or an organization looking to improve the security and efficiency of your data management practices, blockchain-based secure storage and edge computing resource markets for mobile blockchain represent powerful and exciting new tools to help you achieve your goals.

Source image : www.researchgate.net
Source image : www.mdpi.com
Source image : www.mdpi.com


