What new : edge computing be used to improve sustainability

Edge computing is a revolutionary technology that has emerged in recent years to address the needs of the IoT (Internet of Things) and other distributed systems. It is a computing model that involves processing data at or near the source of the data, which provides many benefits over traditional cloud-computing models. Edge computing has the potential to greatly improve sustainability by reducing energy consumption, lowering carbon emissions, and improving resource efficiency. In this article, we will explore the ways in which edge computing can be used to improve sustainability and drive positive environmental outcomes.
Edge Computing for Smart Manufacturing

Abstract
In many industrial applications, the use of edge computing can be a significant enabler for more efficient use of resources, reducing waste, and increasing productivity. By using edge computing, manufacturers can implement real-time monitoring and control of equipment, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. This helps to reduce the amount of energy consumed by equipment, lowering carbon emissions, and improving overall resource efficiency.
Introduction
Smart manufacturing is becoming an increasingly important area for industry, as manufacturers look for ways to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize downtime. One of the key challenges in smart manufacturing is the need to process large volumes of data in real-time, which can be difficult using traditional cloud-based computing models. This is where edge computing comes in, providing an efficient and effective way to process data at or near the source, rather than transmitting it to a central processing center in the cloud. This approach can have a number of benefits for sustainability, including reducing energy consumption, lowering carbon emissions, and improving resource efficiency.
Content
One of the primary ways in which edge computing can be used to improve sustainability in manufacturing is through the implementation of real-time monitoring and control of equipment. By using sensors and other connected devices, it is possible to collect data on the performance of individual machines, and detect any anomalies that may indicate a potential issue. This can help to predict maintenance needs and prevent equipment failure, thereby reducing downtime and minimizing energy consumption.
Edge computing also has the potential to improve the efficiency of overall system performance, by enabling real-time data analysis and decision-making at the edge of the network. This can help to optimize the use of resources, reduce waste, and minimize energy consumption. For example, edge computing can be used to optimize the use of energy in a manufacturing plant, by analyzing data from sensors and identifying areas of waste or inefficiency. This can help companies to reduce their carbon footprint and improve their sustainability performance.
Another key benefit of edge computing for smart manufacturing is the ability to analyze data in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. This can help to minimize the need for frequent repairs or replacement of equipment, which can have a significant impact on the environment. By reducing the frequency of equipment repairs, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and overall resource consumption, while also minimizing the amount of waste generated by the disposal of equipment.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a powerful technology that has the potential to greatly improve sustainability in manufacturing and other industries. By processing data at or near the source, edge computing provides a more efficient and effective way to monitor and control equipment, optimize resource use, and reduce waste. This can have a significant impact on energy consumption, carbon emissions, and overall resource efficiency. As more and more companies begin to adopt edge computing technologies, we can expect to see even greater sustainability benefits in the years to come.
Key Drivers and Benefits of Edge Computing for Smart Manufacturing

Abstract
Edge computing is a key enabler of data analytics and machine learning in smart manufacturing. Its ability to process data at the source, rather than in the cloud, provides a number of benefits for manufacturers, including improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and increased productivity.
Introduction
Edge computing is a new paradigm in computing, which involves processing data at or near the source of the data, rather than transmitting it to a centralized cloud-based processing center. This approach has many advantages for smart manufacturing, as it enables real-time monitoring and control of equipment, reduces the latency associated with cloud-based data processing, and allows for greater scalability and flexibility. In this section, we will explore the key drivers and benefits of edge computing for smart manufacturing.
Content
There are many key drivers of edge computing for smart manufacturing, including the need for real-time data analysis and decision-making, the need for increased flexibility and scalability, and the need to improve overall system performance. By processing data at the edge of the network, rather than transmitting it to a central processing center in the cloud, edge computing can provide real-time insights into the performance of individual machines and enable predictive maintenance. This can help to reduce downtime, minimize energy consumption, and improve overall system efficiency.
In addition, edge computing can help to improve the scalability and flexibility of manufacturing systems, by enabling the use of distributed networks of connected devices. This can help to reduce the cost of deploying and maintaining complex systems, while also providing greater flexibility for future upgrades and enhancements. By using edge computing technologies, manufacturers can create more agile and responsive systems that can adapt to changing business requirements and customer needs.
One of the key benefits of edge computing for smart manufacturing is the ability to improve overall system performance, by providing real-time data analytics and decision-making at the edge of the network. By analyzing data from sensors and other connected devices, it is possible to identify areas of waste or inefficiency, and optimize resource use to reduce costs and improve sustainability. For example, edge computing can be used to optimize the use of energy in a manufacturing plant, by detecting areas of waste and implementing real-time control strategies to minimize energy consumption.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a powerful technology that has the potential to greatly improve the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of smart manufacturing systems. By processing data at or near the source, rather than transmitting it to a central processing center in the cloud, edge computing can provide real-time insights into the performance of individual machines, enable predictive maintenance, and improve overall system efficiency. As more and more manufacturers adopt edge computing technologies, we can expect to see even greater benefits in terms of cost savings, increased productivity, and improved sustainability performance.

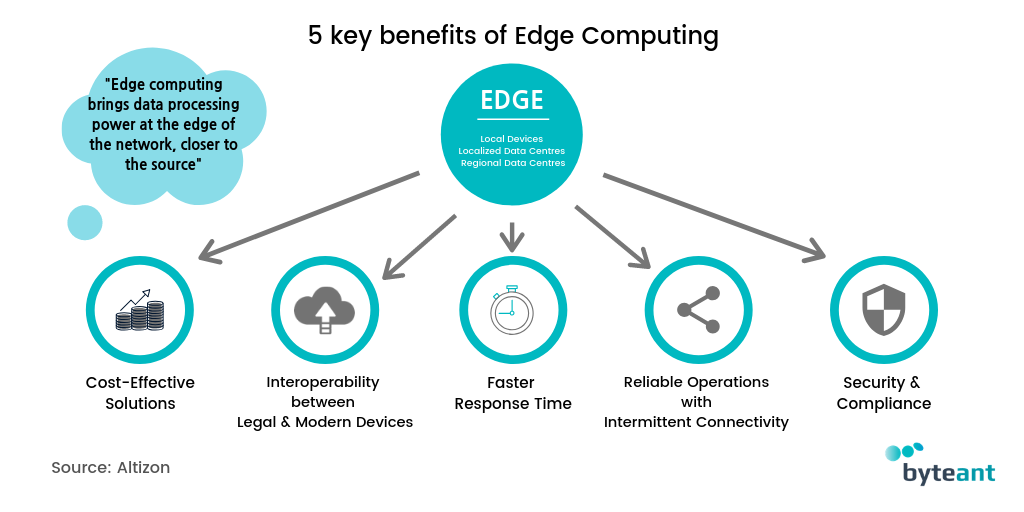
Source image : altizon.com
Source image : www.trentonsystems.com

Source image : sustainability-success.com


