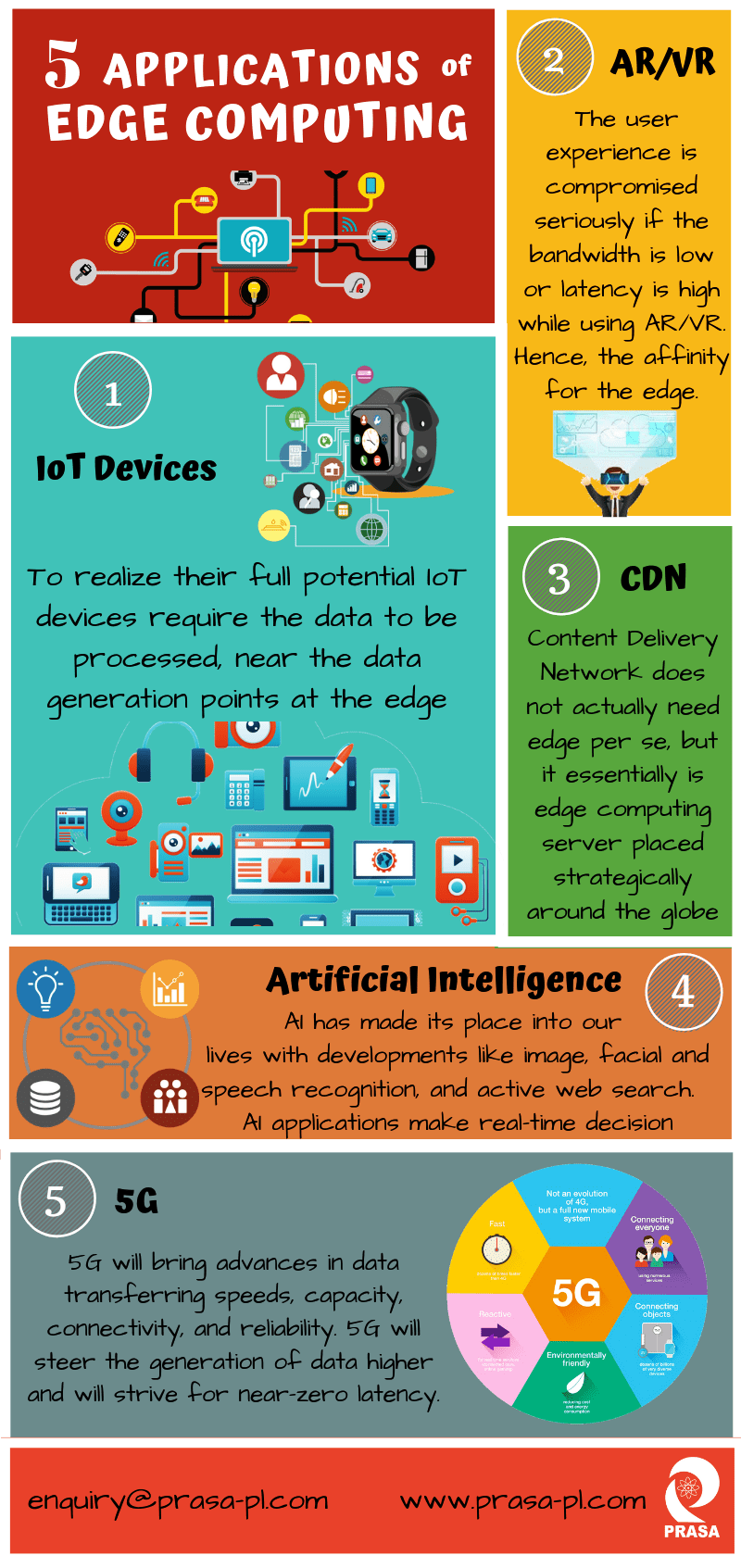
What new : edge computing applications
Hey y’all! Let’s talk about the exciting world of edge computing! Have y’all heard of it? Well, let me tell you, it’s got some amazing applications that are changing the game.
Edge computing applications

Abstract
Edge computing represents a new model of computing that brings data processing and storage closer to the physical location of the data source. By processing data at the edge, edge computing allows for faster response times and reduced latency. This paper explores five key applications of edge computing and the benefits they offer.
Introduction
As we continue to generate more and more data, traditional centralized computing models struggle to keep up with the demand for processing and storage. Edge computing represents a new paradigm for computing that shifts the focus to processing and storing data closer to the source. By bringing computing resources closer to the data source, edge computing allows for faster response times, reduced latency, and improved reliability. In this paper, we will explore five key applications of edge computing and the benefits they offer.
Content
1. Autonomous vehicles
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on real-time data to operate safely and efficiently. With edge computing, the data collected by sensors and cameras on the vehicle can be processed and analyzed in real-time, allowing the vehicle to make split-second decisions. Furthermore, edge computing can help reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted back to a centralized server, reducing network traffic and improving response times.
For example, Ford is using edge computing to power its connected vehicle platform, FordPass. By processing data at the edge, Ford is able to provide real-time pricing and availability for parking spots and gas stations, as well as real-time traffic updates to drivers.
2. Smart cities
Smart cities use IoT devices to collect data on everything from traffic patterns to weather conditions. By processing this data at the edge, cities can make real-time decisions to improve services and reduce costs. For example, in Barcelona, edge computing is being used to optimize the city’s waste management system. Sensors are placed in garbage cans to monitor the fill level, and this data is processed at the edge to create optimal pickup routes for garbage trucks, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
3. Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT applications, such as manufacturing plants or oil rigs, generate massive amounts of data that can overwhelm traditional centralized computing systems. By processing this data at the edge, industry operators can make real-time decisions to improve efficiency and reduce downtime. For example, GE is using edge computing to optimize the performance of wind turbines. By collecting and analyzing data from sensors on the turbines, GE can make real-time adjustments to improve efficiency and reduce maintenance costs.
4. Healthcare
Edge computing is also being used to improve healthcare by processing data from wearable devices and medical equipment in real-time. This allows for faster diagnosis and treatment of patients, and can also help reduce costs by decreasing the need for hospital stays. For example, Philips is using edge computing to monitor patients with chronic conditions, such as COPD or heart disease. By collecting real-time data from wearable devices and analyzing it at the edge, Philips is able to provide patients with personalized treatment plans and reduce hospital readmissions.
5. Retail
Finally, edge computing is being used in the retail industry to improve the shopping experience for customers. By processing data from sensors on products and in-store displays, retailers can personalize the shopping experience for each customer. For example, Macy’s is using edge computing to power its “smart mirrors”. These mirrors use RFID technology to detect the clothing items a customer is trying on, and then display additional information and recommendations on the mirror’s surface.
Conclusion
Edge computing represents a major shift in the way we think about computing. By bringing processing and storage closer to the source of data, edge computing offers faster response times, reduced latency, and improved reliability. The applications of edge computing are numerous and varied, from autonomous vehicles to healthcare. As we continue to generate more and more data, edge computing will play an increasingly important role in the way we process and store that data.
That’s all for now, y’all! Thanks for tuning in to learn about the exciting world of edge computing.

Source image : prasa-pl.com

Source image : www.innominds.com

Source image : www.researchgate.net


