What new : edge computing and iot

As technology continues to evolve, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become a more ubiquitous presence in our lives. The ability to connect everyday devices and gather data has unlocked new possibilities in fields ranging from healthcare to transportation.
Edge Computing: Enhancing the IoT Experience
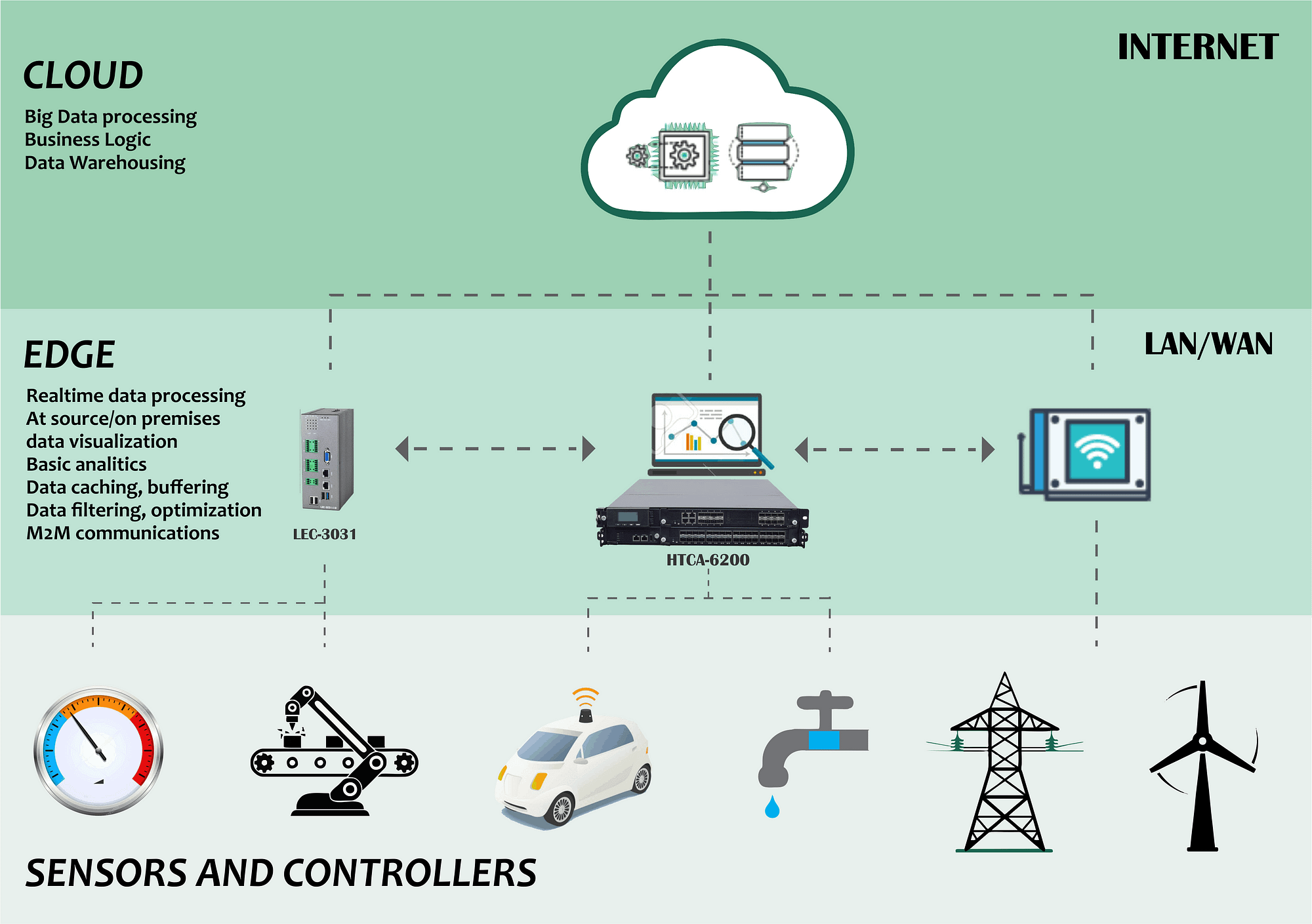
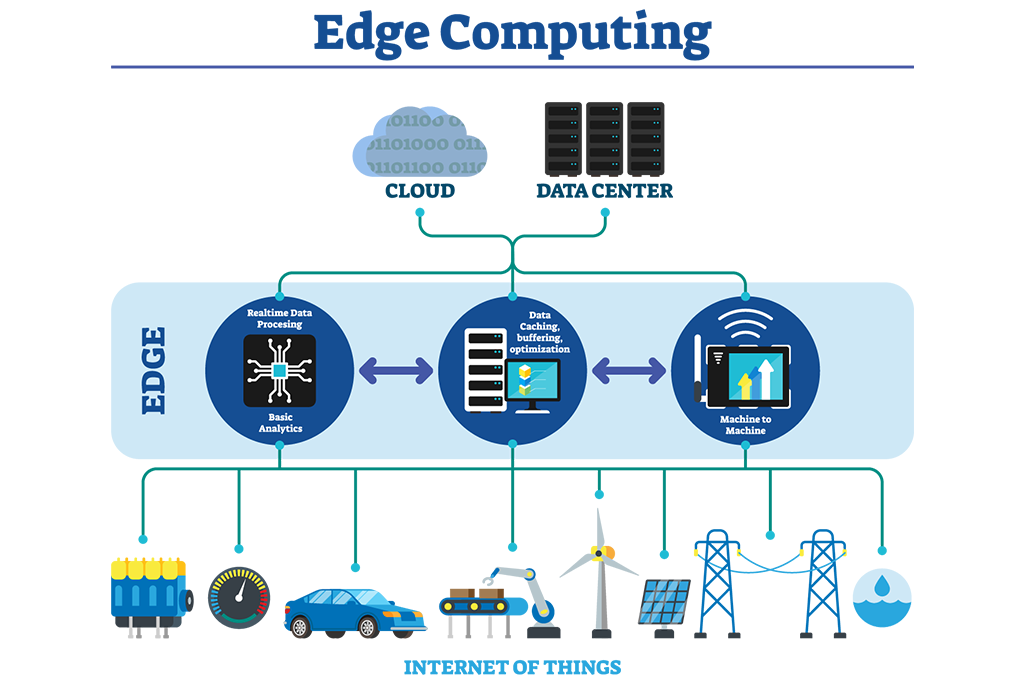
One of the latest technologies to emerge in the IoT space is edge computing. As the name suggests, edge computing involves processing data at the edge of the network, as close to the source as possible. By doing so, edge computing can reduce latency, increase security, and decrease the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud for analysis.
Abstract
This article explores the benefits of edge computing for the IoT, and how it can help to enhance the user experience. We also discuss the challenges of implementing edge computing, and explore some common use cases.
Introduction
Edge computing is becoming increasingly popular in the IoT space. By bringing processing power closer to the source of data, edge computing can help to solve some of the biggest challenges facing the IoT. These challenges include latency, security, and the sheer amount of data being generated.
One of the biggest benefits of edge computing is reduced latency. By processing data at the edge, we can eliminate the delay that occurs when data is sent to the cloud for analysis. This is particularly important in applications that require real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation systems.
Another major benefit of edge computing is increased security. By keeping sensitive data on-site, rather than sending it to the cloud for analysis, we can reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. This is particularly important in applications where data privacy is a concern, such as healthcare or finance.
Finally, edge computing can help to reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud for analysis. This is particularly important in applications where bandwidth is limited, such as in remote or rural areas.
Content
Now that we’ve discussed the benefits of edge computing, let’s look at some common use cases for this technology.
Smart Home Automation
One of the most popular applications for the IoT is smart home automation. By connecting household devices to the Internet, we can create a home that is more efficient, convenient, and secure.
Edge computing can help to enhance the smart home experience in a number of ways. For example, by processing data locally, we can reduce latency and ensure that actions are taken in real-time. This is particularly important in applications like security, where a delay of even a few seconds could be disastrous.
Another benefit of edge computing in smart homes is increased privacy. By keeping data on-site, rather than sending it to the cloud for analysis, we can reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. This is particularly important in applications like security cameras or smart locks, where privacy is a major concern.
Industrial Automation
Another major application for the IoT is industrial automation. By connecting machines and sensors in factories and other industrial settings, we can create a more efficient and productive environment.
Edge computing can help to enhance industrial automation in a number of ways. For example, by processing data locally, we can reduce latency and ensure that actions are taken in real-time. This is particularly important in applications like predictive maintenance, where delays could result in costly downtime.
Another benefit of edge computing in industrial automation is increased security. By keeping sensitive data on-site, rather than sending it to the cloud for analysis, we can reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. This is particularly important in applications like control systems or robotics, where the consequences of a security breach could be catastrophic.
Autonomous Vehicles
Perhaps one of the most exciting applications for the IoT is autonomous vehicles. By connecting vehicles to the Internet, we can create a transportation system that is safer, more efficient, and more convenient.
Edge computing can help to enhance the autonomous vehicle experience in a number of ways. For example, by processing data locally, we can reduce latency and ensure that actions are taken in real-time. This is particularly important in applications like collision avoidance, where delays could result in accidents.
Another benefit of edge computing in autonomous vehicles is increased security. By keeping sensitive data on-site, rather than sending it to the cloud for analysis, we can reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. This is particularly important in applications like vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication or remote vehicle control, where security is critical.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a powerful technology that has the potential to significantly enhance the IoT experience. By processing data at the edge of the network, we can reduce latency, increase security, and decrease the amount of data being transmitted to the cloud.
Of course, implementing edge computing is not without its challenges. For example, edge devices may have limited processing power or storage capacity, which can make it difficult to perform complex analytics. Additionally, managing edge devices can be challenging, as they may be located in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
Despite these challenges, edge computing is rapidly becoming a key technology in the IoT space. As more and more devices come online, and as the demand for real-time responses and increased privacy grows, we can expect to see edge computing become an increasingly important part of the IoT ecosystem.
References
- Wired: WTF is Edge Computing?
- Network World: What is Edge Computing?
- InfoWorld: Edge Computing Explained
- ECN Magazine: How Edge Computing is Improving the IoT Experience

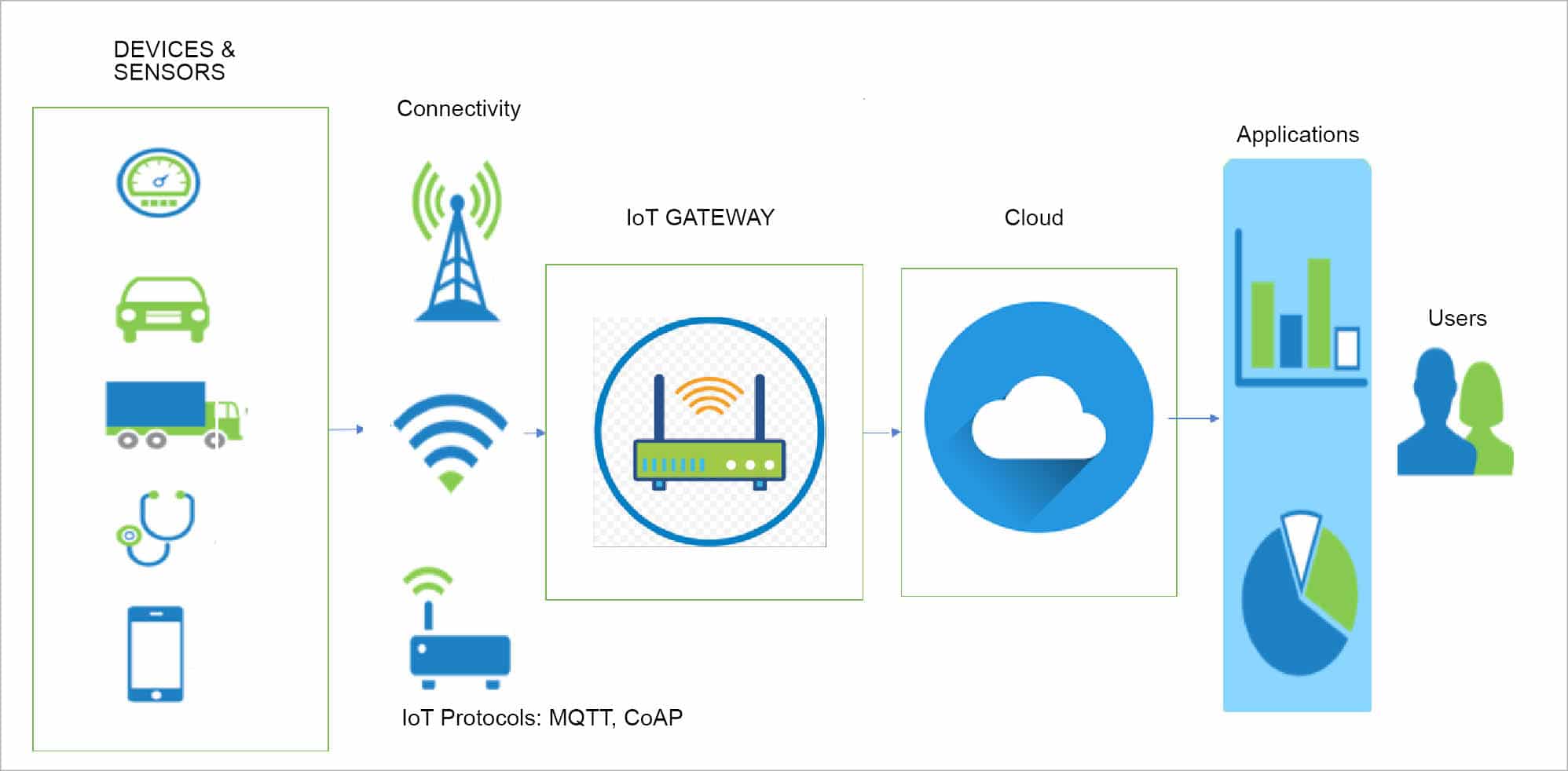
Source image : www.opensourceforu.com
Source image : innovationatwork.ieee.org

Source image : medium.com


