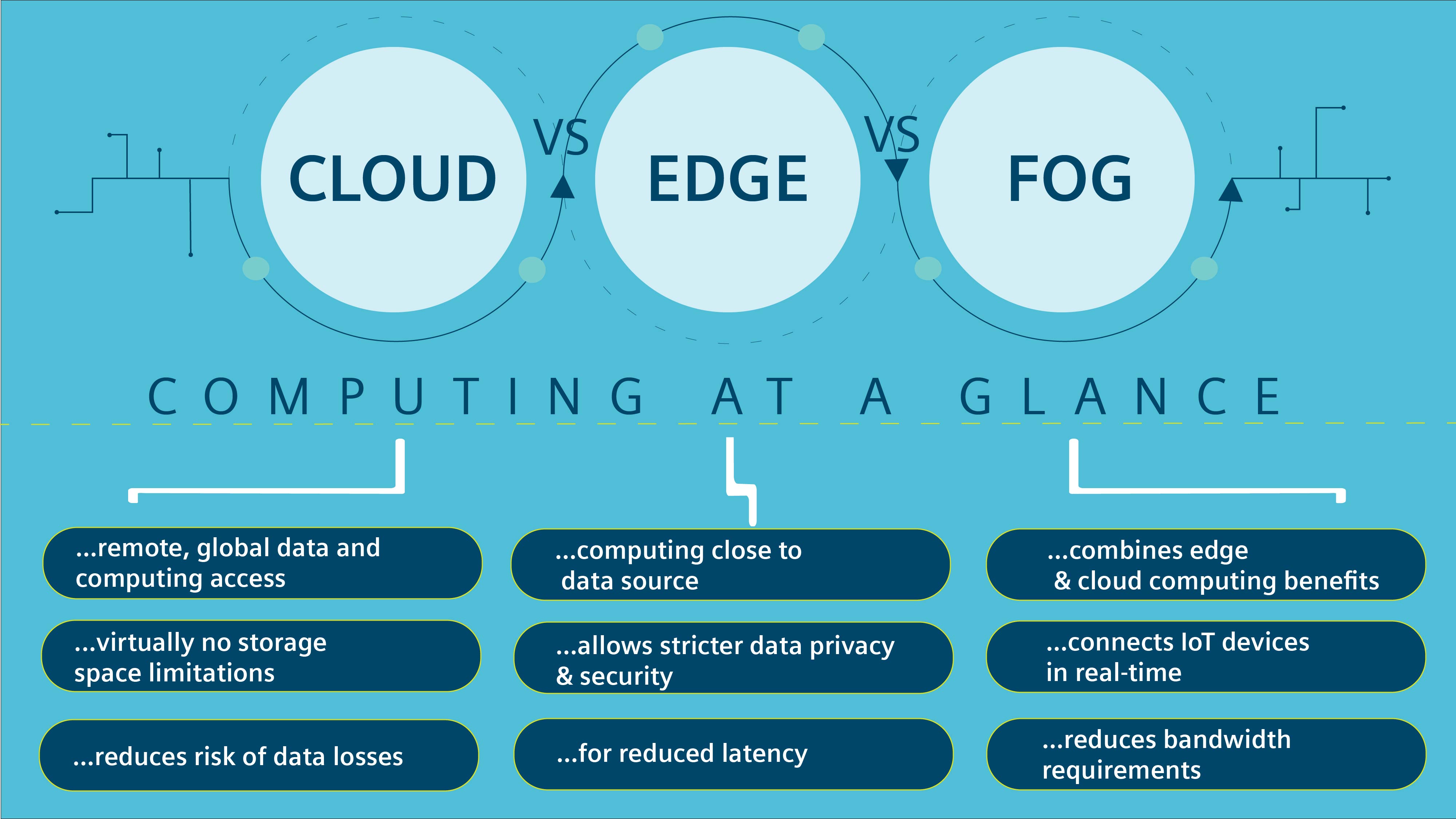
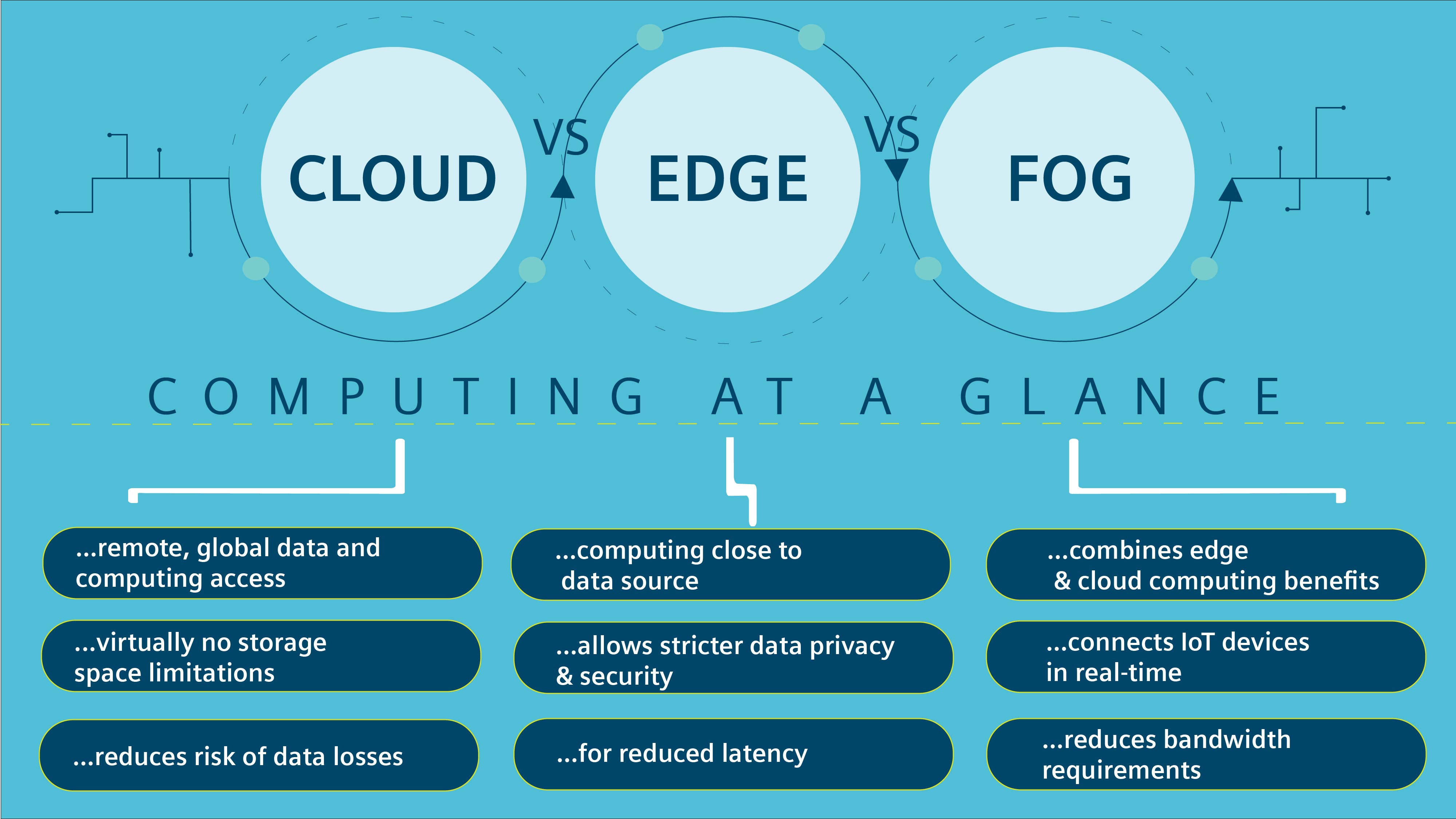
What difference between edge computing and cloud computing

In today’s fast-paced world, technology is advancing at an unprecedented rate. With the advent of edge computing and cloud computing, businesses are confronted with the question of which platform to choose. Let’s explore the benefits and drawbacks of each platform and see how they can be beneficial for financial services.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing framework that locates computation and data storage at the edge between the data source and the cloud. This means that computations and data storage are performed closer to the source of data, which can be a device, a sensor, or an IoT-enabled endpoint. The primary benefits of edge computing are lower latency, reduced bandwidth, improved reliability, and enhanced privacy.

Abstract
Edge computing can provide benefits to financial institutions in a number of ways, including faster processing, improved customer experiences, and reduced security risks. By using edge computing, financial institutions can improve the speed of their transactions and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Introduction
Financial services companies require a fast and reliable infrastructure to provide their customers with the best possible experience. However, this can be challenging because of the complex nature of financial transactions, which require high-speed processing and a secure environment. With the emergence of edge computing, financial institutions have the opportunity to streamline their processes, reduce costs, and improve customer experiences. In this article, we will explore the benefits and drawbacks of edge computing and see how it can be beneficial for financial services.
Content
Benefits of Edge Computing for Financial Services
One of the primary benefits of edge computing for financial services is faster transaction processing. Financial institutions often deal with a large volume of transactions, and processing them in real-time using cloud computing can be time-consuming. With edge computing, financial institutions can perform computations and data storage closer to the source of the data, which reduces latency and improves speed.
Edge computing can also improve customer experiences by providing faster access to data and information. This is especially important in the financial services industry, where customers expect quick and efficient service. By using edge computing, financial institutions can reduce the time required to process transactions, which can result in improved customer satisfaction.
Another benefit of edge computing is improved security. With edge computing, data is processed and stored locally, which reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. In addition, edge computing can provide additional security features, such as encryption and authentication, which can further protect sensitive financial data.
Drawbacks of Edge Computing for Financial Services
While edge computing can provide many benefits, there are also some drawbacks that financial institutions should consider. One of the primary drawbacks is the complexity of managing edge infrastructure. Edge computing requires a distributed architecture, which can be difficult to manage and maintain. In addition, edge computing requires specialized skills, which can be costly and difficult to acquire.
Another drawback of edge computing is the limited scalability. Edge computing is designed to handle a limited number of devices and data sources, which can be an issue in financial services, where processing large amounts of data is common. This means that financial institutions may need to invest in additional infrastructure to support their growing business needs.
Finally, edge computing can be more expensive than cloud computing, especially when it comes to hardware and maintenance. Financial institutions need to carefully consider the cost-benefit of using edge computing versus cloud computing, and determine which platform is the most cost-effective for their needs.
Conclusion
Edge computing can provide many benefits to financial institutions, including faster processing, improved customer experiences, and enhanced security. However, there are also some drawbacks that need to be considered, such as the complexity of managing edge infrastructure and the limited scalability. Financial institutions need to carefully evaluate the cost-benefit of using edge computing versus cloud computing, and determine which platform is the most appropriate for their needs.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a centralized computing framework that locates computation and data storage on remote servers. This means that computations and data storage are performed in a remote location, which can be accessed by clients over the internet. The primary benefits of cloud computing are scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of management.
Abstract
Cloud computing has become increasingly popular in the financial services industry because of its scalability, flexibility and cost-effectiveness. By using cloud computing, financial institutions can reduce their infrastructure costs, while also providing faster and more efficient services to their customers. In this article, we will explore the benefits and drawbacks of cloud computing for financial services and see how it can be beneficial for financial services.
Introduction
Financial services companies have traditionally used on-premises infrastructure to manage their data and applications. However, with the rise of cloud computing, financial institutions are now adopting cloud-based solutions to reduce costs and improve efficiency. In this article, we will explore the benefits and drawbacks of cloud computing for financial services and see how it can be beneficial for financial services.
Content
Benefits of Cloud Computing for Financial Services
One of the primary benefits of cloud computing for financial services is scalability. Cloud computing allows financial institutions to quickly and easily scale their infrastructure up or down based on their business needs. This means that financial institutions can quickly respond to changes in demand, without having to invest in additional infrastructure.
Cloud computing can also provide financial institutions with greater flexibility. Cloud-based solutions can be accessed from anywhere, which means that financial institutions can provide their services to customers more efficiently. In addition, cloud computing can provide financial institutions with greater agility, which is important in an increasingly competitive market.
Another benefit of cloud computing is cost-effectiveness. Cloud computing can eliminate the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure, which can significantly reduce costs. In addition, cloud computing can provide financial institutions with greater efficiency and productivity, which can further reduce costs and improve profitability.
Drawbacks of Cloud Computing for Financial Services
While cloud computing can provide many benefits, there are also some drawbacks that financial institutions should consider. One of the primary drawbacks is the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Cloud-based services are not immune to attacks, and financial institutions need to carefully evaluate the security of their cloud service providers.
Another drawback of cloud computing is the potential for vendor lock-in. Financial institutions that use cloud-based services may be dependent on their service providers, which can limit their ability to switch to alternative providers. This can be a concern for financial institutions that need to maintain control over their operations and data.
Finally, there may be regulatory compliance issues with cloud computing. Financial institutions need to ensure that their cloud service providers comply with all relevant regulations and standards, such as PCI DSS and GLBA.
Conclusion
Cloud computing can provide many benefits to financial institutions, including scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of management. However, there are also some drawbacks that need to be considered, such as the risk of data breaches and vendor lock-in. Financial institutions need to carefully evaluate the cost-benefit of using cloud computing versus edge computing, and determine which platform is the most appropriate for their needs.
In conclusion, both edge computing and cloud computing have their own unique benefits and drawbacks. Financial institutions need to carefully evaluate their business needs and determine which platform can provide them with the most value. Whether it’s edge computing, cloud computing or a combination of both, financial institutions need to be agile and flexible, in order to respond to changing market conditions and stay ahead of their competitors.
Source image : www.analyticsvidhya.com

Source image : www.deltecbank.com
Source image : www.siemens-advanta.com


