cloud and edge computing

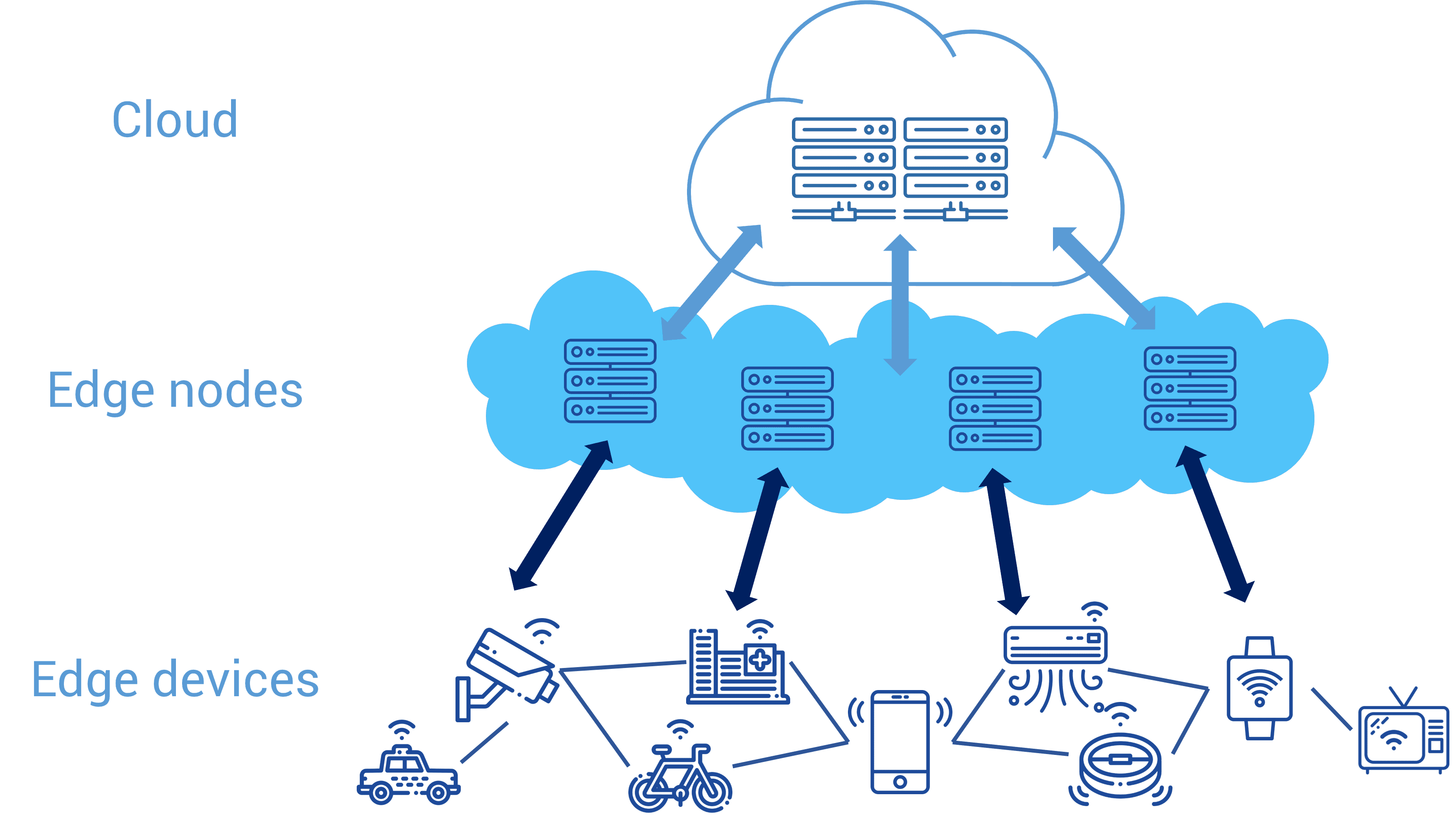
#image_title
Are you currently using cloud computing? Then it’s time to make the move to edge computing!
The Future is Here with Edge Computing
The world of technology is constantly evolving, and edge computing is the latest development you need to follow. Instead of relying on a centralized cloud to process data, edge computing brings that processing closer to the source of the data. This reduction in latency and bandwidth usage means quicker decisions, better security, and more reliable systems.
A Comprehensive Ecosystem

The edge computing ecosystem encompasses a wide range of technology, from sensors to the centralized cloud. This comprehensive ecosystem provides developers with the necessary tools to design and deploy complex applications. With this approach, the data is collected and analyzed as close to the source as possible. This not only speeds up decision-making but reduces errors that might occur during longer processing times.
Abstract
Edge computing is a technological concept that is quickly gaining traction in today’s rapidly advancing world. Instead of processing large amounts of data on central servers, edge computing processes data on micro data centers or edge servers located closer to the source of the data. The ability to create mini data centers all over the world, while maintaining centralized control, is proving to be a major advantage in implementing edge computing solutions. This essay will highlight some of the benefits to be gained from edge computing and provide valuable insights about the future of this technology.
Introduction
As technology continues to advance, businesses and users alike are beginning to demand faster processing speeds, lower latency, and greater overall reliability. This has led to the emergence of edge computing as a groundbreaking new solution. Unlike traditional cloud computing solutions that rely on a centralized data center network to store and process data, edge computing brings the processing closer to the devices generating it.
When comparing edge computing to cloud computing, it’s easy to see why the former has become a strong contender. In traditional cloud computing, data is transmitted from the device generating the data to a centralized cloud data center. This method can lead to slow processing times, data security concerns, and high bandwidth usage, among other issues. For businesses, this can result in higher overhead costs and slow response times that may impair their performance or competitiveness.
Edge computing seeks to solve these problems by processing data close to the source. This approach decreases the time it takes to process the data, reduces overall network bandwidth usage, and significantly lowers the risk of data breaches. With this model, edge computing ensures information is processed quickly and securely, allowing businesses to better serve customers, make faster decisions, and reduce costs.
The Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing offers a number of benefits over traditional cloud computing solutions. Besides boosting processing speeds, reducing latency, and increasing reliability, here are some additional benefits:
- Improved security: As mentioned, edge computing processes data in a decentralized manner, which makes it harder to attack than a centralized model. This is because the data is processed closer to the device, and there are fewer points of failure. Malware and other cyber threats are less likely to pose a problem, as they will have to travel through multiple layers of security to reach the data.
- Easy setup: Deploying an edge computing solution is relatively simple, as it does not require the building of extensive infrastructure. Rather, it is made up of numerous small infrastructure setups spread over a wider network, which means more flexibility and ease of deployment. Companies can set up edge servers in remote areas without worrying about network connectivity issues.
- Scalability: Edge computing allows for the quick deployment of a large number of resources exactly where they are needed. Unlike traditional cloud solutions, which may require companies to send data back and forth between different data centers, edge computing enables companies to easily scale their infrastructure to meet the unique needs of their business.
- Better cost management: Since data is processed closer to the source, the overall cost of data transfer is significantly reduced. This can lead to lower network infrastructure costs and lower usage fees for remote data transfer. Businesses can also save on resources and energy costs, since they don’t have to maintain a massive centralized data center.
Use Cases for Edge Computing
Edge computing has numerous use cases across different industries, including but not limited to:
- Telecommunications and the Internet of Things (IoT): Edge computing can speed up data processing in IoT devices like sensors, thereby facilitating real-time decision-making. Telecom companies can use edge computing to build digital networks that stream videos and music more efficiently.
- Manufacturing and Industrial IoT (IIoT): Edge computing can be used in manufacturing to monitor production lines or track product performance, while IIoT can use it to optimize factory production time and reduce equipment downtime.
- Smart cities: Edge computing can be used to process data that drives the smart city infrastructure, which includes traffic and waste management, security systems, and public transport.
Challenges with Edge Computing
While edge computing offers several benefits, it is not without its challenges, including:
- High costs: Although deploying edge computing involves less infrastructure, deploying the number of micro data centers needed on a global scale can still involve significant costs, which may make it less accessible for small or medium-sized businesses.
- Uptime: Edge computing relies on maintaining connectivity between the devices and data center. If this connection is lost, the device might be unable to access the data it needs to operate, resulting in service downtime.
- Data processing and transfer: Edge computing can pose a challenge when it comes to data processing and transfer, particularly if the data is complex or has to be aggregated across multiple sources. Edge computing systems also require more equipment than traditional cloud computing setups, which can be expensive and difficult to maintain.
Conclusion
Edge computing is an exciting technological innovation that can revolutionize the way businesses and users interact with data. While it’s not without its challenges, when properly deployed, edge computing can lead to faster processing times, better security, and more reliable systems. It is becoming increasingly clear that edge computing is the future of computing, and the benefits of adopting it are numerous, including reduced costs, improved scalability, and increased network efficiency.
Businesses that want to thrive in today’s fast-paced world need to embrace new technologies that enable faster, more efficient, and more reliable data processing. With edge computing, businesses can effectively handle their data-related needs and benefit from the many advantages that it offers.
Source image : towardsdatascience.com
Source image : www.alibabacloud.com

Source image : www.cbinsights.com


