chromosome microarray

What you need to know before ordering chromosomal microarray
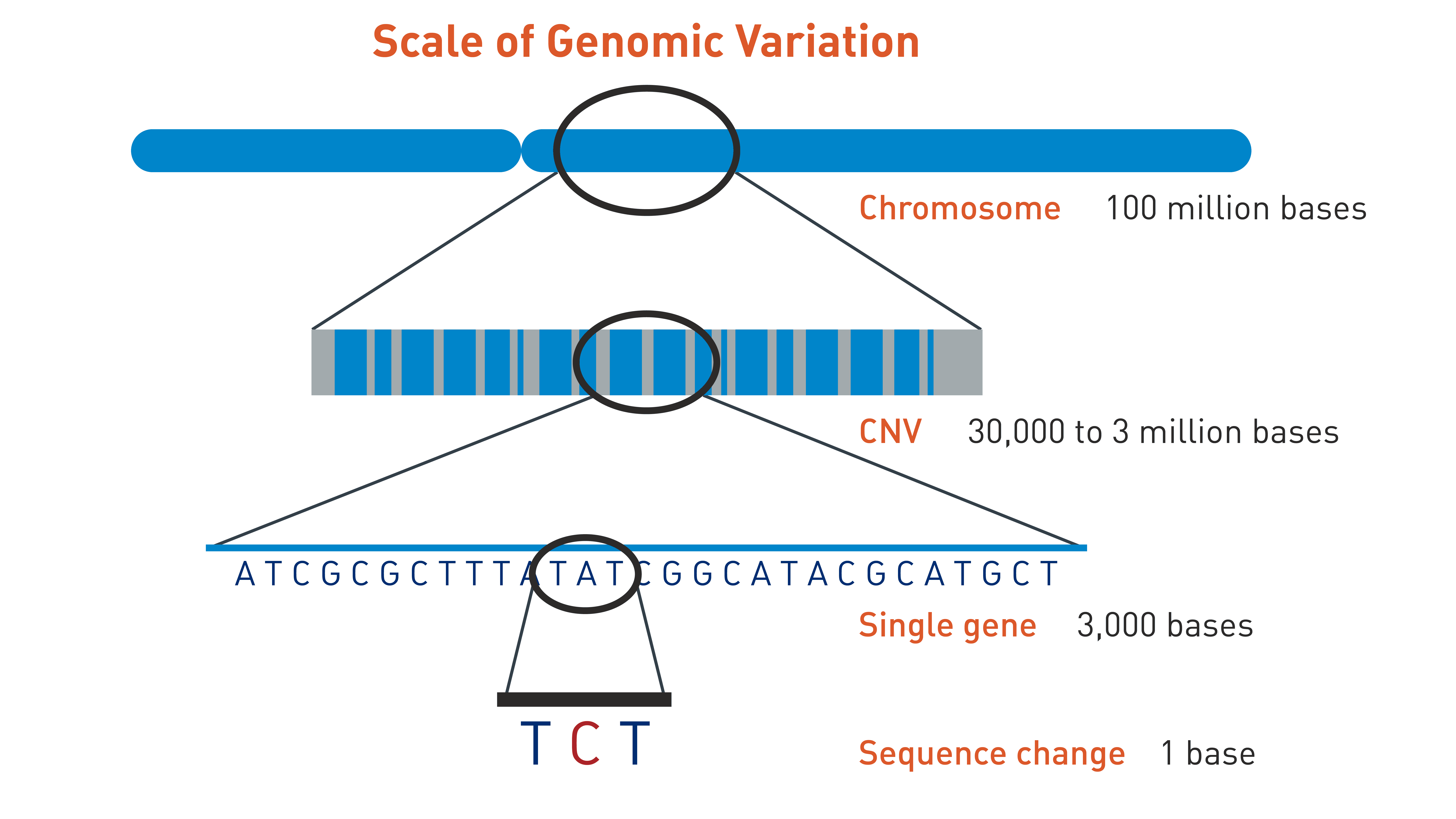
Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) is a powerful diagnostic tool that has revolutionized the way we diagnose genetic disorders. CMA is a technique that allows us to detect deletions and duplications in the DNA that are too small to be seen with traditional karyotyping. This technique has a higher resolution than karyotyping, allowing for the detection of smaller copy number variations (CNVs), which has led to the identification of new genetic disorders.
The use of chromosomal microarray for prenatal diagnosis

Chromosomal microarray
Abstract
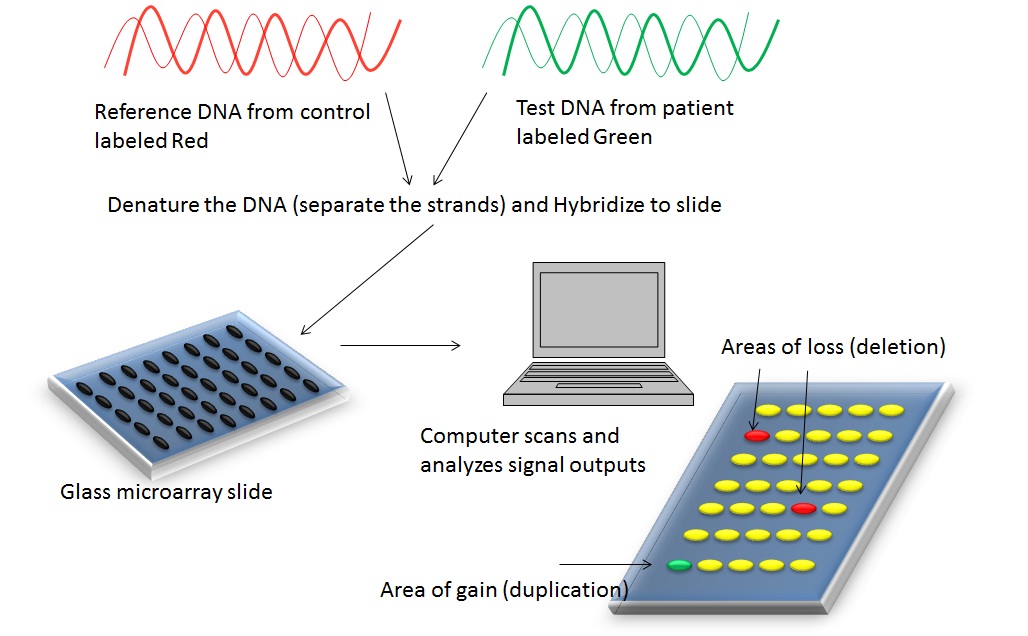
Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) is a powerful tool for the diagnosis of genetic disorders. CMA allows the detection of small CNVs that traditional karyotyping cannot identify. CMA has revolutionized the diagnosis of genetic disorders, leading to the identification of new disorders and improving our understanding of the underlying genetic causes of known disorders. CMA has also become an important tool for prenatal diagnosis, allowing for the detection of CNVs that could result in serious health consequences for the fetus. This article discusses what you need to know before ordering CMA.
Introduction
Genetic disorders can be caused by a variety of different genetic mutations, including chromosomal abnormalities such as deletions and duplications. Chromosomal abnormalities can lead to serious health consequences, including developmental delays, intellectual disabilities, and birth defects. Traditional karyotyping, which involves staining chromosomes and examining them under a microscope, has been the standard diagnostic tool for identifying chromosomal abnormalities. However, karyotyping has limitations, including a low resolution, which means it cannot detect deletions and duplications that are too small to be seen.
Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) is a powerful diagnostic tool that overcomes the limitations of karyotyping. CMA is a technique that involves analyzing the DNA of an individual to detect any CNVs. CMA has a much higher resolution than karyotyping, allowing for the detection of smaller CNVs. This has led to the identification of new genetic disorders and has improved our understanding of the underlying genetic causes of known disorders.
Content
If you are considering ordering CMA for your patient, there are several things you need to know.
Indications for CMA
CMA is indicated for patients with a suspected genetic disorder. This includes patients with intellectual disability, developmental delay, autism spectrum disorder, and birth defects. CMA is also indicated for patients with multiple congenital anomalies and those with a family history of genetic disorders.
Sample types
CMA can be performed on several different sample types, including blood, amniotic fluid, chorionic villus sampling (CVS), and products of conception. Blood is the most commonly used sample type for CMA, as it is non-invasive and easy to obtain. Amniotic fluid and CVS samples are obtained during pregnancy and can provide information about the genetic health of the fetus. Products of conception samples are obtained after a miscarriage or abortion and can provide information about the genetic cause of the loss.
Limitations of CMA
While CMA is a powerful diagnostic tool, it does have limitations. CMA cannot detect all types of genetic mutations, including mutations in single genes. CMA is also not able to detect balanced chromosomal rearrangements, such as translocations, inversions, and insertions. In addition, CMA cannot detect epigenetic changes, such as DNA methylation, which can also contribute to the development of genetic disorders.
Interpretation of results
Interpreting the results of CMA can be complex and requires specialized knowledge and training. The results of CMA can identify CNVs that are potentially pathogenic, benign, or of uncertain clinical significance. In addition, some CNVs can have variable expressivity, which means that they can lead to different clinical outcomes in different individuals. It is important to discuss the results of CMA with a genetic counselor or medical geneticist to ensure that they are correctly interpreted.
Cost and insurance coverage
The cost of CMA can vary widely depending on the laboratory performing the test and the type of sample being analyzed. In general, CMA is more expensive than karyotyping. However, CMA is often covered by insurance when it is ordered for medically necessary reasons. It is important to check with the patient’s insurance company before ordering CMA to determine if it is covered.
Conclusion
Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) is a powerful diagnostic tool that has revolutionized the way we diagnose genetic disorders. CMA allows for the detection of small CNVs that traditional karyotyping cannot identify. If you are considering ordering CMA for your patient, it is important to understand the indications for CMA, the limitations of the test, and how to interpret the results. It is also important to discuss the risks and benefits of CMA with the patient and to ensure that the test is covered by insurance when it is ordered for medically necessary reasons.

Source image : www.jax.org

Source image : geneticseducation.ca

Source image : www.ajog.org




