chromosome 2 fusion intelligent design

Have you ever wondered how humans evolved from chimpanzees? There have been many theories over the years, but one model in particular has stirred up controversy. This model suggests that humans and chimpanzees share a common ancestor and that over time, natural selection led to physical and genetic differences that resulted in the two distinct species we see today.
The Human Chromosome #2 Controversy
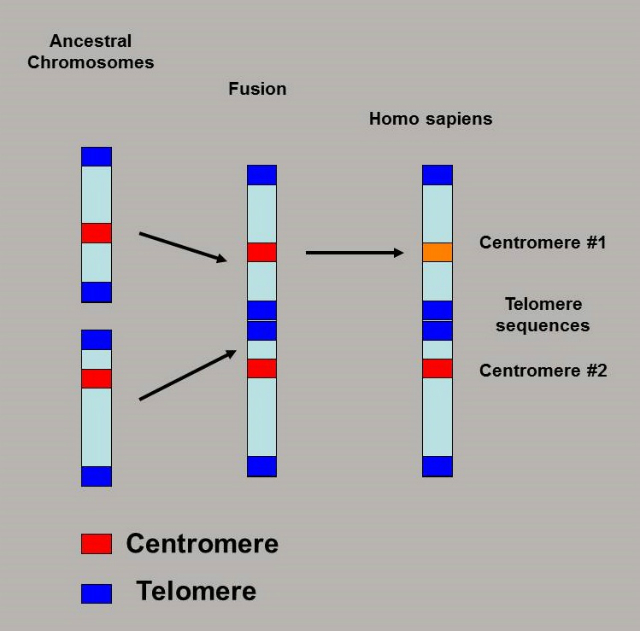
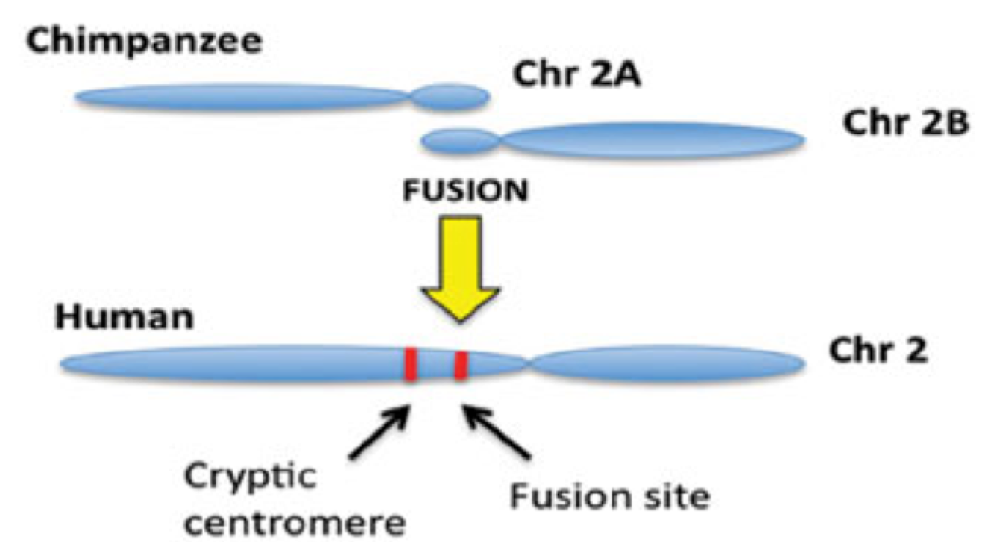
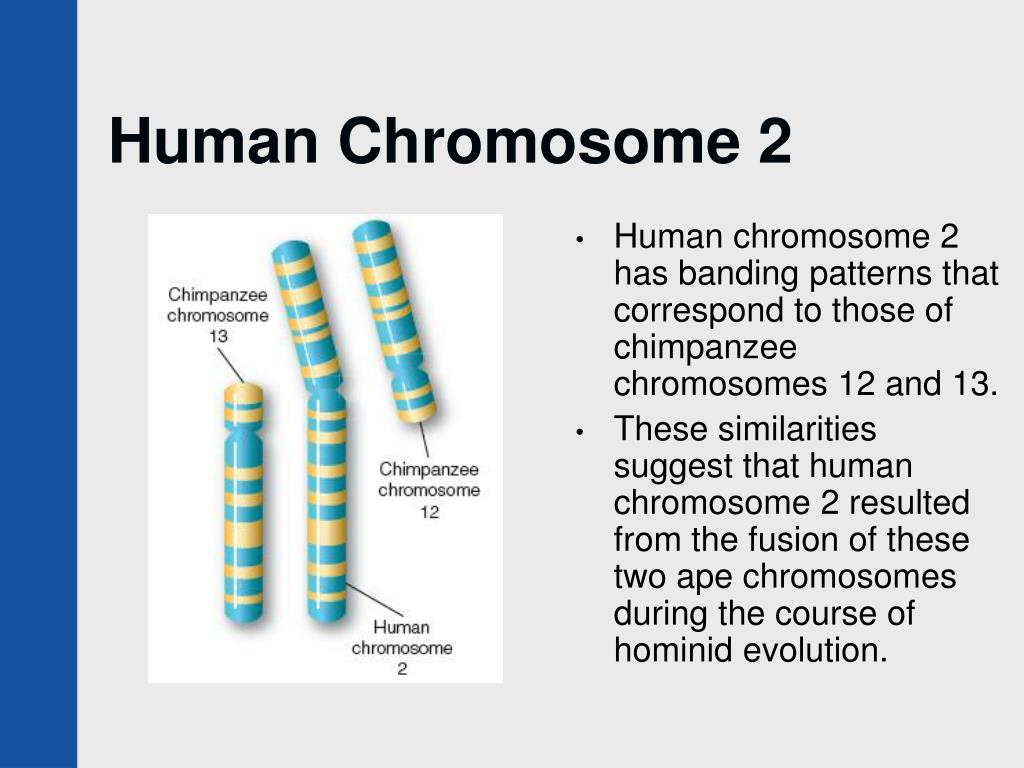
One of the most compelling pieces of evidence for this theory is the human chromosome #2. This chromosome is unique in that it appears to be the result of a fusion event between two smaller chromosomes that are found in other primate species, including chimpanzees. This finding suggests that humans and chimpanzees shared a common ancestor that had these two separate chromosomes. However, some scientists have questioned whether this fusion event actually occurred and whether the genetic anomalies found in human chromosome #2 could have arisen from other factors.
Abstract
In this article, we will explore the evidence for and against the chimp to human evolution model, with a particular focus on the controversial human chromosome #2. We will examine the genetic and physical differences between humans and chimpanzees and consider how these could have arisen through natural selection. We will also address the criticisms of this theory and explore alternative explanations for the genetic similarities and differences between the two species. Ultimately, we will argue that the evidence supports the chimp to human evolution model and that the human chromosome #2 provides compelling evidence of our shared ancestry with chimpanzees.
Introduction
For decades, scientists have been studying the genetic and physical differences between humans and chimpanzees in an attempt to understand how we evolved from a common ancestor. One of the most compelling pieces of evidence for this theory is the human chromosome #2, which appears to be the result of a fusion event between two smaller chromosomes that are found in other primate species, including chimpanzees. This finding suggests that humans and chimpanzees shared a common ancestor that had these two separate chromosomes, and that over time, natural selection led to the fusion of these two chromosomes in the human lineage.
However, some scientists have questioned whether this fusion event actually occurred and whether the genetic anomalies found in human chromosome #2 could have arisen from other factors. Some have suggested that the genetic similarities between humans and chimpanzees could be the result of common design rather than common ancestry, while others have pointed to the possibility of convergent ancestry, which suggests that the genetic similarities could have arisen independently in humans and chimpanzees.
Content
Despite these criticisms, there is a wealth of evidence that supports the chimp to human evolution model, including the similarities in DNA sequences, the shared genetic anomalies, and the physical similarities between humans and chimpanzees. For example, humans and chimpanzees share over 98% of their DNA, indicating a very close evolutionary relationship. Additionally, scientists have identified numerous shared genetic anomalies between humans and chimpanzees, including the fusion of the two smaller chromosomes that make up human chromosome #2.
Furthermore, there are many physical similarities between humans and chimpanzees that suggest we share a common ancestor. For example, both species have opposable thumbs, which are essential for grasping objects and manipulating tools. Both species also have forward-facing eyes, which are important for depth perception and binocular vision. Additionally, both species have the ability to communicate using complex vocalizations and body language, which suggests that we share a common communication system.
Another piece of evidence that supports the chimp to human evolution model is the fossil record. Over the years, scientists have unearthed numerous fossils that provide insights into the evolutionary history of our species. These fossils reveal a gradual progression of physical changes over time, from early hominids with ape-like features to modern humans with distinctively human characteristics. This gradual progression is consistent with the idea that humans evolved from a common ancestor with chimpanzees and other primates.
Despite these findings, there are still some scientists who remain skeptical of the chimp to human evolution model. Some argue that the genetic similarities between humans and chimpanzees could be the result of common design rather than shared ancestry, while others suggest that convergent evolution could explain the genetic similarities. However, these criticisms have been largely refuted by the scientific community, and the evidence continues to support the idea that humans and chimpanzees share a common ancestor.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the chimp to human evolution model has been the subject of much debate and controversy over the years. However, the evidence overwhelmingly supports the idea that humans and chimpanzees share a common ancestor and that over time, natural selection led to the physical and genetic differences that distinguish the two species today. While there may still be some uncertainty surrounding the details of this evolutionary history, the evidence is clear that humans and chimpanzees are closely related and that we share a common ancestry. The discovery of the human chromosome #2 provides compelling evidence of this shared ancestry and underscores the importance of continued research into our evolutionary history.
Source image : www.tasc-creationscience.org
Source image : www.slideserve.com

Source image : www.publish0x.com




