instructional theory and technology for the new paradigm of education

As educators, we all want to find the most effective ways to help our students learn. One way to achieve this is by incorporating various learning theories into our instructional practices. In this post, we will explore three prominent learning theories and how they can be implemented in the English Language Arts (ELA) classroom.
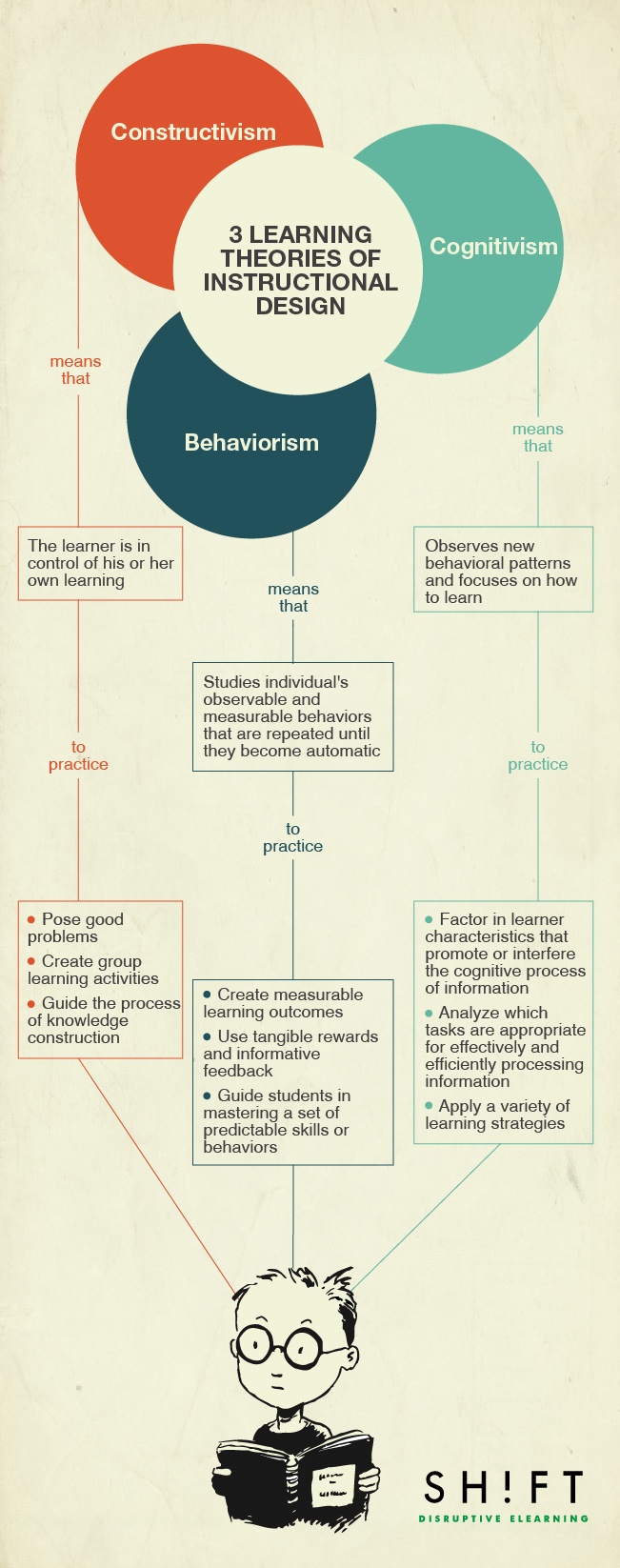
Learning Theories of Instructional Design
Abstract
Instructional design is a crucial aspect of education that focuses on creating effective learning experiences for students. One way to achieve this is by understanding and implementing different learning theories. In this post, we will explore the three primary learning theories of instructional design: behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism. We will explain each theory’s key ideas and how they can be incorporated into the English Language Arts (ELA) classroom. By the end of this post, you will have a solid understanding of how to create effective instructional design that aligns with different learning theories.
Introduction
Effective instructional design requires an understanding of how people learn. Learning theories explain how people learn and provide a foundation for designing effective teaching and learning experiences. Three prominent learning theories are behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism. In the ELA classroom, each of these theories can be applied in different ways, depending on the lesson’s objectives and the students’ needs.
Behaviorism

Abstract
Behaviorism is a learning theory that suggests learners respond to stimuli in their environment, leading to specific outcomes. It emphasizes the importance of reinforcement and punishment in shaping behavior. Behaviorism can be applied in the English Language Arts (ELA) classroom by focusing on developing essential skills such as reading comprehension and writing fluency. This theory can be applied in various ways, including direct instruction, modeling, and feedback loops.
Content
One way to apply behaviorism in the ELA classroom is through direct instruction. This strategy involves explicitly teaching a skill or concept and providing students with feedback on their performance. For example, a teacher may model how to write an effective thesis statement and then provide students with a writing prompt to practice this skill. The teacher would then provide feedback on each student’s thesis statement, reinforcing correct responses while correcting errors.
Another way to incorporate behaviorism in the ELA classroom is through modeling. Modeling involves demonstrating a particular skill or behavior for students to emulate. For instance, a teacher could model how to read closely and annotate a text, showing students how to identify key details and make connections between ideas. Students could then practice this skill, with the teacher providing feedback and reinforcement for effective annotations.
Lastly, feedback loops are a critical aspect of behaviorism. Effective feedback helps students understand what they did well and how they can improve. In the ELA classroom, this could involve providing feedback on a written assignment or in-class discussion. Teachers could identify where students demonstrated the expected behaviors and where they could improve, reinforcing effective responses and correcting errors.
Cognitivism
Abstract
Cognitivism emphasizes the importance of the mind in the learning process, focusing on how learners process and organize information. This learning theory suggests that individuals actively construct knowledge through their experiences, and that learning occurs when these experiences are connected to individuals’ existing knowledge and understanding. In the ELA classroom, cognitivism can be applied by encouraging critical thinking skills and providing opportunities to connect new information to existing knowledge.
Content
Cognitivism places a significant emphasis on critical thinking skills, which are essential in the ELA classroom. One way to encourage critical thinking skills is by providing opportunities for students to analyze information and make connections across different texts. For instance, teachers could assign a comparative essay where students are asked to compare and contrast two texts, identifying similarities and differences.
Another way to incorporate cognitivism in the ELA classroom is by encouraging metacognition. Metacognition involves thinking about one’s thinking and is a critical aspect of the learning process. Teachers can promote metacognition by asking students to reflect on their learning, identify their strengths and weaknesses, and set goals for future learning.
Lastly, cognitivism underscores the importance of connecting new information to existing knowledge. In the ELA classroom, this could involve asking students to activate prior knowledge before reading a new text or encouraging them to make connections between different texts. Teachers could also provide opportunities for students to summarize and synthesize information, reinforcing connections and integrating new learning into existing knowledge structures.
Constructivism

Abstract
Constructivism is a learning theory that suggests learners construct knowledge through their experiences and interactions with their environment. This theory emphasizes the importance of learners’ active participation in the learning process and suggests that learning occurs best in a social context. In the ELA classroom, constructivism can be applied by providing opportunities for hands-on, experiential learning and group work.
Content
Constructivism emphasizes the importance of hands-on, experiential learning in the ELA classroom. One way to incorporate this theory is by providing opportunities for students to engage with texts through drama, role-playing, or other creative activities. For instance, students could act out a scene from a play or write and perform their own spoken word poem.
Another way to apply constructivism in the ELA classroom is through group work. Group work encourages learners’ active participation in the learning process and provides opportunities for collaboration and social learning. For instance, students could work in groups to analyze a text or create their own written work. Teachers could provide guidance and support as needed, encouraging the constructive sharing of ideas and reinforcing effective collaboration skills.
Lastly, constructivism stresses the importance of context in the learning process. Teachers can promote contextualized learning by providing real-world examples that connect to students’ experiences and interests. This approach can help students see the relevance of the concepts they are learning and provide motivation for further learning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, incorporating various learning theories in instructional design can help to create effective learning experiences for students. Behaviorism emphasizes reinforcement and punishment in shaping behavior, cognitivism underscores the importance of the mind in processing and organizing information, and constructivism emphasizes learners’ active participation in constructing knowledge through experiences and interactions with their environment.
In the ELA classroom, each theory has its unique strengths and can be applied in various ways, depending on the lesson’s objective and the students’ needs. By understanding these theories and their applications, educators can create learning experiences that help students develop essential skills and knowledge, encouraging critical thinking, creativity, and a lifelong love of learning.

Source image : educationaltechnology.net

Source image : msabigailholmes.wordpress.com

Source image : itchronicles.com






