edge computing for autonomous driving

Edge computing is one of the hottest topics in the world of technology. It refers to the concept of bringing computing resources closer to where the data is generated and consumed, rather than relying on centralized data centers alone. This allows for faster processing, lower latency, and improved performance for applications and services that require real-time data processing. In this post, we will explore the benefits of edge computing and how it is changing the way that companies approach their IT infrastructure.
The Benefits of Edge Computing
One of the main advantages of edge computing is improved performance. By processing data closer to the source, applications and services can operate with lower latency, which means faster response times and a better user experience. This is particularly important for services that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation systems, and augmented reality applications.
Edge computing also helps to reduce network congestion and bandwidth usage. Instead of sending all data to a centralized data center for processing, only the relevant data is sent. This means that network traffic is reduced, which can lead to lower costs and improved performance. It also means that organizations can process data without relying on a high-speed internet connection, which can be particularly useful in remote or areas with limited connectivity.
Abstract
Edge computing is an innovative technology that brings computing resources closer to where the data is generated and consumed. This allows for faster processing, lower latency, and improved performance for applications and services that require real-time data processing. In this post, we have explored the benefits of edge computing and how it is changing the way that companies approach their IT infrastructure.
Introduction
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and other real-time data-intensive applications has led to an explosion in the demand for computing resources. Traditional data centers are no longer sufficient for processing the vast quantities of data generated by these applications. This has led to a growing interest in edge computing, which allows organizations to bring computing resources closer to where the data is generated and consumed.
Content
Lower Latency and Improved Performance
One of the main benefits of edge computing is improved performance. By processing data closer to the source, applications and services can operate with lower latency, which means faster response times and a better user experience. This is particularly important for services that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation systems, and augmented reality applications.
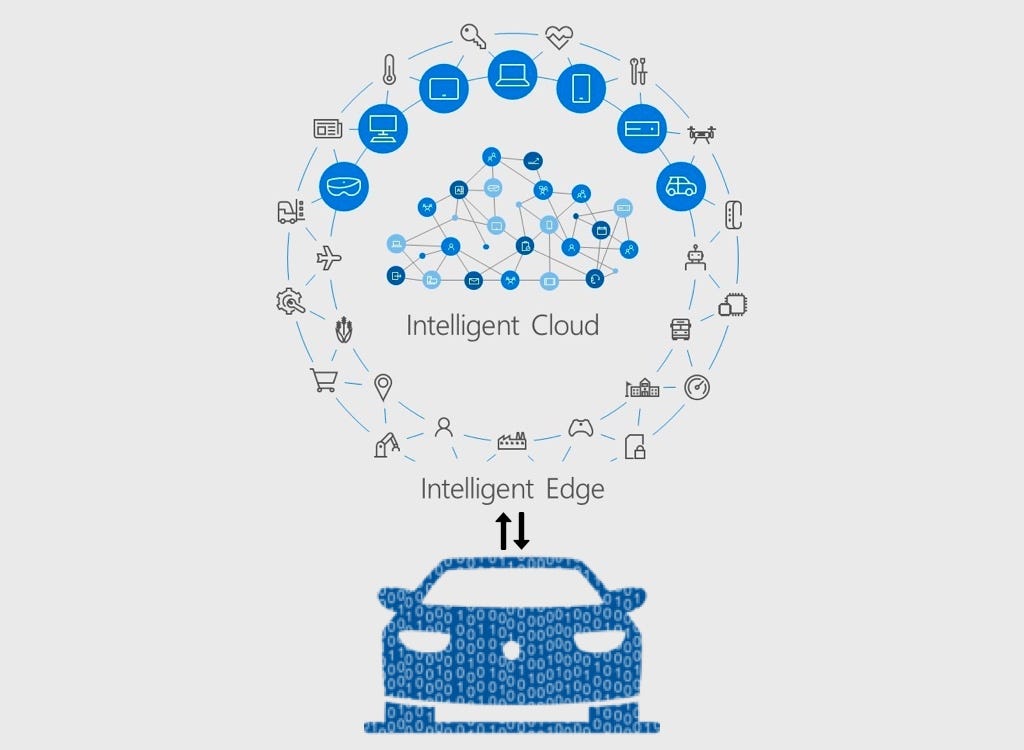
For example, consider an autonomous vehicle that needs to process large amounts of data in real-time. If the vehicle were to rely on a centralized data center, it would need to send all of the data to the data center for processing, which would result in significant latency. This latency could lead to safety issues, particularly in situations where split-second decisions need to be made. By using edge computing, the vehicle can process the data locally, which reduces the latency and improves performance.
Reduced Network Congestion and Bandwidth Usage
Another benefit of edge computing is reduced network congestion and bandwidth usage. Instead of sending all data to a centralized data center for processing, only the relevant data is sent. This means that network traffic is reduced, which can lead to lower costs and improved performance. It also means that organizations can process data without relying on a high-speed internet connection, which can be particularly useful in remote or areas with limited connectivity.
For example, consider a mining company that needs to monitor the performance of its equipment in real-time. If the company were to rely on a centralized data center for processing, it would need to send all of the data generated by its equipment to the data center, which could be located hundreds or thousands of miles away. This would result in significant latency and bandwidth usage, which could lead to higher costs and reduced performance. By using edge computing, the company can process the data locally, which reduces the latency and bandwidth usage.
Increased Security and Privacy
Edge computing can also improve security and privacy. By processing data locally, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and other security threats. This is because the data does not need to leave the local network, which reduces the risk of interception or other unauthorized access. It also means that organizations can maintain greater control over their data, which can be particularly important for applications that involve sensitive or confidential information.
For example, consider a hospital that needs to monitor the health of its patients in real-time. If the hospital were to rely on a centralized data center for processing, it would need to send all of the data generated by its patients to the data center, which could be located hundreds or thousands of miles away. This would increase the risk of data breaches and other security threats. By using edge computing, the hospital can process the data locally, which reduces the risk of data breaches and other security threats.
Cost Savings
Edge computing can also lead to cost savings for organizations. By reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent to a centralized data center for processing, organizations can reduce their bandwidth usage and data storage costs. This can be particularly useful for organizations that generate large amounts of data, such as those in the industrial and manufacturing sectors. By using edge computing, these organizations can process the data locally, which reduces the amount of data that needs to be sent to a centralized data center for processing.
Conclusion
Edge computing is an innovative technology that is changing the way that organizations approach their IT infrastructure. By bringing computing resources closer to where the data is generated and consumed, edge computing offers a range of benefits, including improved performance, reduced network congestion and bandwidth usage, increased security and privacy, and cost savings. As the demand for real-time data processing continues to grow, it is likely that more organizations will turn to edge computing to meet their IT needs.
Image Credits:
Image 1:

Image 2:

Source image : medium.com

Source image : www.proximus.be

Source image : www.01net.it


