difference between fog and edge computing

#image_title
There has been a lot of buzz lately in the tech industry regarding the shift towards edge and fog computing. But what do these terms really mean and how are they different from traditional cloud computing? In this post, we’ll explore the differences between edge and fog computing and how these innovations are revolutionizing the way we process data.
Edge Computing
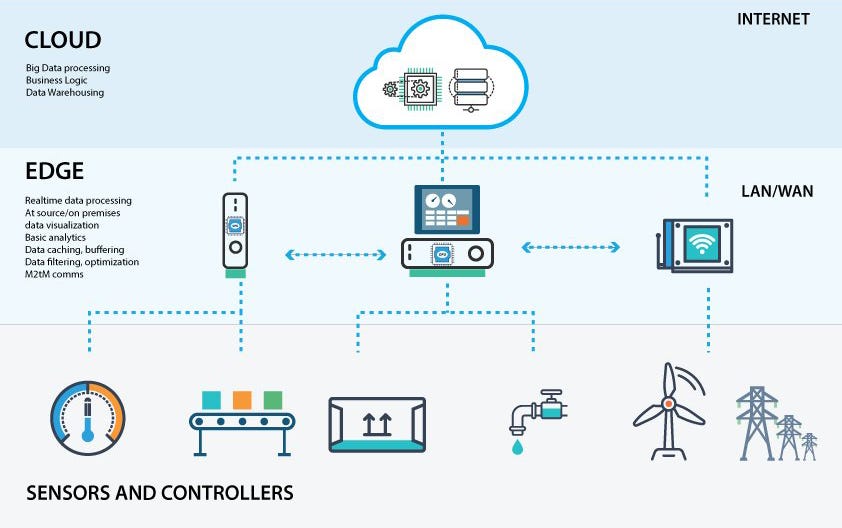
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data at or near the point of collection, rather than sending it to a centralized server or data center. This approach is particularly useful for applications that require low latency, such as real-time streaming video, gaming, and IoT devices. By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the need for long-distance data transmission, thereby improving network efficiency and reducing costs.
Abstract
Edge computing is a promising technology that offers a wide range of benefits, including reduced latency and improved network efficiency. By processing data at or near the point of collection, edge computing is helping to drive innovation in a variety of industries.
Introduction
Over the past few years, we’ve seen a growing trend towards edge computing in the tech industry. With the rise of IoT devices, real-time streaming video, and other applications that require low latency, edge computing is becoming an increasingly popular alternative to traditional cloud computing. In this post, we’ll explore the differences between edge and fog computing and how these innovations are revolutionizing the way we process data.
Content
Traditionally, data was processed and stored at centralized data centers, far away from the point of collection. However, as the number of IoT devices and other applications that rely on real-time data processing has increased, this approach has become increasingly inefficient.
Edge computing offers a more efficient way to process data by allowing it to be processed at or near the point of collection. This reduces the need for long-distance data transmission, which can cause delays and increase costs. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce latency and improve network efficiency.
One key benefit of edge computing is its ability to support real-time applications, such as video streaming and gaming. With traditional cloud computing, data must be transmitted to a centralized data center, processed, and then sent back to the user. This can result in delays and poor performance, particularly in applications that require low latency. However, with edge computing, data can be processed locally, ensuring that these applications have the speed and performance necessary to operate in real-time.
Edge computing is also well-suited to IoT applications, which often involve large volumes of data that must be processed in real-time. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over a network, thereby improving network efficiency and reducing costs.
Fog Computing
While edge computing refers to processing data at or near the point of collection, fog computing takes this approach one step further by processing data at the network edge. Fog computing involves the use of distributed computing resources, such as routers, switches, and other network devices, to process data in real-time. By processing data closer to the network edge, fog computing can reduce latency and improve performance.

Abstract
Fog computing is a powerful technology that extends the benefits of edge computing by processing data at the network edge. By leveraging distributed computing resources, fog computing can help organizations reduce latency and improve network efficiency.
Introduction
While edge computing has been getting a lot of attention lately, it’s important not to overlook the power of fog computing. By processing data at the network edge, fog computing can help organizations reduce latency and improve performance. In this section, we’ll explore the differences between edge and fog computing and how these technologies are driving innovation in the tech industry.
Content
While edge computing involves processing data at or near the point of collection, fog computing takes things one step further by processing data at the network edge. This approach involves using distributed computing resources, such as routers, switches, and other network devices, to process data in real-time. By processing data closer to the network edge, fog computing can reduce latency and improve performance.
Fog computing is particularly well-suited to applications that involve large volumes of data that need to be processed in real-time. This includes applications in industries such as healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing. By processing data at the network edge, fog computing can help organizations improve response times and reduce the risk of data loss.
Another benefit of fog computing is its ability to support applications that require real-time analytics. By processing data at the network edge, fog computing can provide real-time insights into data, enabling organizations to make faster, more informed decisions. This is critical for applications such as predictive maintenance, where even minor delays can result in costly equipment failures.
Conclusion
Edge and fog computing are two of the most exciting developments in the tech industry in recent years. By processing data at or near the point of collection, these technologies are improving network efficiency, reducing latency, and driving innovation in a variety of industries. While there are some differences between edge and fog computing, both are powerful tools that have the potential to transform the way we process and analyze data.

Source image : www.differencebetween.net

Source image : medium.com

Source image : www.e-zigurat.com


