difference between cloud fog and edge computing

#image_title
Today’s technological advancements have made it possible for us to store and access vast amounts of data easily. However, this level of data storage and management requires more than just traditional computing methods. Enter the world of cloud, edge, and fog computing. In this post, we will be exploring the practical applications of these three computing methods and how each plays an important role in moving the data industry forward.
Practical Applications of Cloud, Edge, and Fog Computing
Cloud computing is an online platform that provides a wide range of services such as storage, software, and databases to users who can access them from anywhere with an internet connection. Some of the most practical applications of cloud computing include:

Online Storage and Sharing
Cloud computing allows users to store and share data online. With cloud storage, users can securely store their data without having to worry about storage limitations on their local devices. They can also share files with others through the cloud and collaborate in real-time.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS allows businesses to access software applications that would otherwise be too expensive for them to purchase and maintain. Instead, the software is hosted in the cloud and users can access it through a web browser or mobile app. This model has been adopted by a number of popular software applications, including Microsoft Office 365 and Google Drive.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is a cloud computing service that offers virtual machines, storage, and networking resources to customers. It is often used by businesses that have limited physical infrastructure but still require access to powerful computing resources on a temporary or medium-term basis.
Now, let’s explore the world of edge computing.
Edge Computing
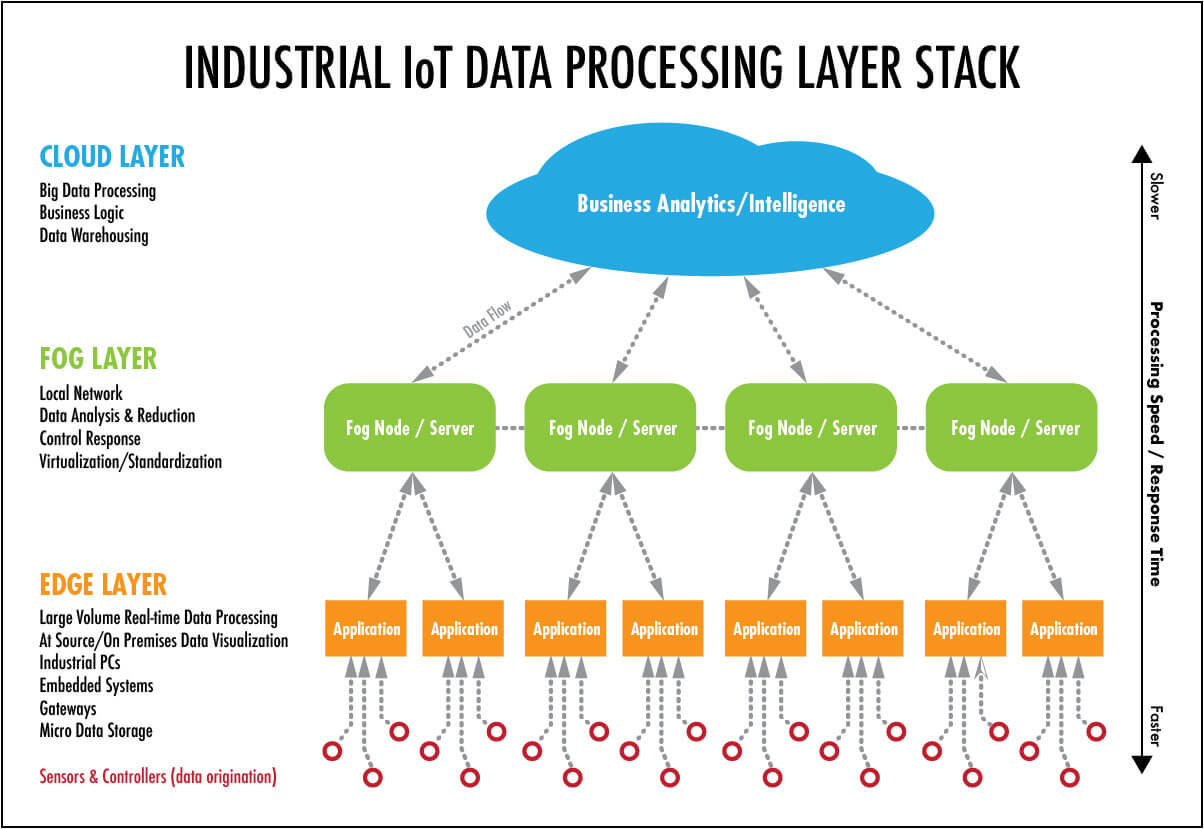
Edge computing is a computing model that is designed to process data at or near the source of the data generation. This model is becoming increasingly popular due to its ability to reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud for processing. Some of the most practical applications of edge computing include:
![[Discussion post]Need of Cloud,Fog and Edge Computing - Huawei](https://forum.huawei.com/enterprise/en/data/attachment/forum/202106/18/053915atc8mwow88oh816z.jpg?Cloud_fog_edge-e1503328057334.jpg)
Internet of Things (IoT)
Edge computing plays a crucial role in processing data generated by IoT devices. With edge computing, data is processed and analyzed in real-time, allowing businesses to rapidly respond to changes in the environment they operate in. Therefore, edge computing is a must-have for businesses that operate in fast-moving industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and logistics.
Autonomous Vehicles
Edge computing is essential to the functioning of autonomous vehicles. These vehicles generate vast amounts of data, which needs to be processed in real-time for the vehicle to make decisions quickly and safely. Edge computing allows this processing to happen in real-time, rather than needing to send the data to the cloud for processing, which would take too long and hinder the vehicle’s ability to make decisions in time.
Smart Grids
Edge computing can help improve the efficiency and reliability of smart grids. With an edge computing infrastructure, data is processed in real-time, enabling the system to adjust to changes in supply and demand, and reduce the potential for power outages.
So far, we have explored the benefits of cloud and edge computing. Now, let’s dive into what fog computing has to offer.
Fog Computing
Fog computing is similar to edge computing, but with a slightly different approach. It is a distributed computing paradigm that brings cloud computing capabilities closer to the data source. Fog computing allows us to move beyond the traditional boundaries of edge computing and provides an intermediary layer between edge devices and cloud backend services. The most practical applications of fog computing include:
Real-time Analytics
Fog computing enables device data to be analyzed and acted upon in real-time. This is particularly important for systems that require rapid responses to changing data, such as video surveillance systems that need to identify and respond to potential threats in real-time.
Distributed Data Processing
With fog computing, devices can process data locally and share the results with each other. This means that devices can collaborate and learn from each other’s experiences, which improves overall system performance.
Reduced Data Transport
Fog computing reduces the amount of data that needs to be transported to and from the cloud. This reduces the load on the cloud and provides faster responses to users without requiring users to have high-bandwidth connections all the time.
Conclusion
Cloud, edge, and fog computing offer unique benefits to businesses and organizations. Cloud computing provides a wide range of services that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, while edge computing processes data at or near the source of data generation. Fog computing extends the capabilities of edge computing by bringing cloud computing capabilities closer to the data source. Choosing the right computing solution depends on the specific needs of your organization. So stay up-to-date on the latest computing trends and find the solution that best suits you.
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this post informative and insightful. If you have any comments or questions regarding this topic, feel free to leave them in the comments section below.

Source image : www.e-zigurat.com

Source image : forum.huawei.com
Source image : www.winsystems.com


