5g edge computing use cases

#image_title
Five Edge Computing Use Cases

Abstract
Edge computing is a new technology that enables the processing of data at the edge of the network, rather than in the cloud or in a remote data center. It can be used for a wide range of applications, including IoT, industrial automation, gaming, AI and more.
Introduction
Edge computing is becoming an increasingly important technology in the world of IT. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), there is a growing need to process data at the edge of the network, closer to the device or application generating the data. Edge computing enables this by bringing the computing power and storage closer to where it is needed, rather than relying on remote data centers and cloud infrastructure.
In this article, we will explore five different use cases for edge computing, covering a range of industries and applications.
Content
Use Case #1: Industrial Automation
Industrial automation is an area where edge computing can have a major impact. By processing data at the edge of the network, manufacturing facilities can improve efficiency, reduce downtime and improve quality control.
For example, in a typical manufacturing plant, there may be thousands of sensors and devices generating data. This data can be used to monitor production processes, detect anomalies and perform predictive maintenance. However, processing all of this data in the cloud or in a remote data center can be slow and unreliable. By using edge computing, the data can be processed in real-time, enabling faster decision-making and more efficient operation.
Edge computing can also be used to improve safety in industrial environments. For example, by processing data from cameras and sensors in real-time, edge computing can be used to detect safety hazards, such as workers in dangerous locations or unsafe machine conditions. This can reduce the risk of accidents and improve worker safety.
Use Case #2: Smart Cities
Smart cities are another area where edge computing can have a major impact. By processing data at the edge of the network, cities can improve infrastructure, reduce traffic congestion and improve public safety.
For example, by using edge computing to process data from sensors and cameras, cities can improve traffic flow by adjusting traffic lights in real-time based on current conditions. Edge computing can also be used to detect and respond to public safety incidents, such as accidents or natural disasters.
Additionally, edge computing can be used to improve energy efficiency in buildings and public spaces. By processing data from sensors and devices, edge computing can be used to optimize lighting, heating and cooling systems, reducing energy waste and lowering costs.
Use Case #3: Healthcare
Healthcare is another area where edge computing can have a major impact. By processing data at the edge of the network, healthcare providers can improve patient care, reduce costs and improve efficiency.
For example, edge computing can be used to monitor patient vital signs in real-time, enabling early detection of health issues and reducing the risk of complications. Edge computing can also be used to analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRI scans, in real-time, enabling faster diagnosis and treatment.
Furthermore, edge computing can be used to improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery. For example, by processing data from patient records and medical devices, edge computing can be used to automate administrative tasks, such as scheduling appointments and ordering medication.
Use Case #4: Gaming
Gaming is an area where edge computing can provide a major advantage. By processing game data at the edge of the network, gamers can experience faster response times and reduced latency, improving the overall gaming experience.
For example, by using edge computing to process game data in real-time, gamers can experience faster response times and reduced lag. This is particularly important for multiplayer games, where fast response times can make the difference between winning and losing.
Additionally, edge computing can be used to improve the performance of gaming hardware. By offloading some of the processing from the device to the edge, gaming devices can run more efficiently and with less heat buildup.
Use Case #5: AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are two areas where edge computing is becoming increasingly important. By processing data at the edge of the network, AI and machine learning applications can be faster and more accurate, improving the overall performance of these applications.
For example, edge computing can be used to process data from cameras and sensors in real-time, enabling faster and more accurate object recognition. This is particularly important for applications such as autonomous vehicles, where quick and accurate decisions must be made based on real-time data.
Additionally, edge computing can be used to improve the privacy and security of AI and machine learning applications. By processing data locally, rather than sending it to the cloud, sensitive data can be kept safe and secure.
Conclusion
Edge computing is an exciting new technology with a wide range of applications. From industrial automation to smart cities and gaming, edge computing has the potential to bring processing power and storage closer to where it is needed, enabling faster decision-making and more efficient operation. As more organizations begin to adopt edge computing, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases in the future.
Solutions for the 5G and IoT Edge Computing Revolution
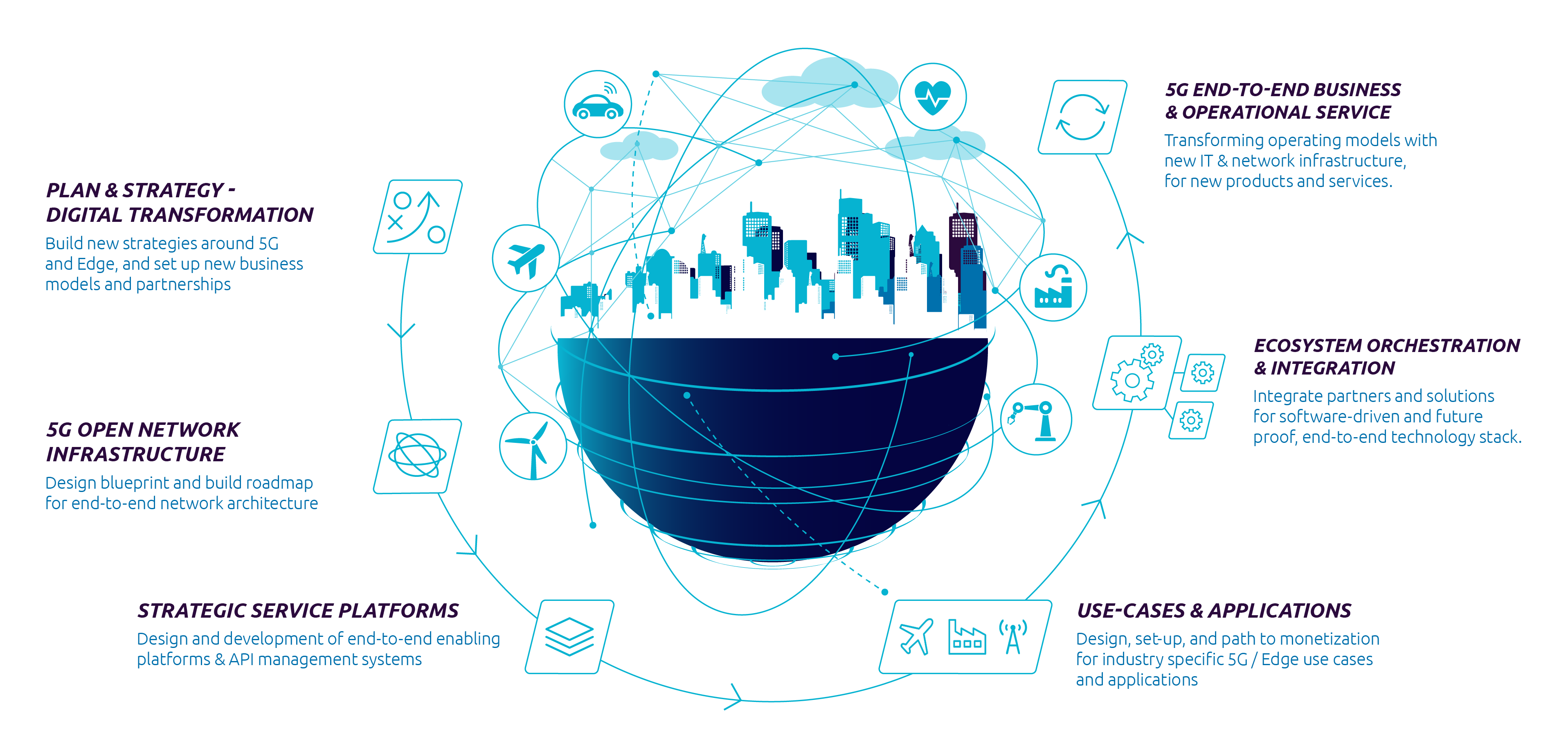
Abstract
The revolution of 5G and IoT is bringing about dramatic changes to the way in which data is processed, stored and utilized. Edge computing is a crucial technology in this new era, enabling faster decision-making, reduced latency and increased security. In this article, we will explore some of the key solutions for the 5G and IoT edge computing revolution.
Introduction
The rise of 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) is bringing about a revolution in the way in which data is processed, stored and utilized. With the exponential growth of data generated by IoT devices, there is a growing need for a new approach to processing this data. Edge computing is a critical technology that enables processing of data at the edge of the network, closer to the device or application generating the data. This can lead to faster decision-making, reduced latency, and increased security.
In this article, we will explore some of the key solutions for the 5G and IoT edge computing revolution.
Content
Solution #1: Distributed Cloud
Distributed cloud is one of the key solutions for the 5G and IoT edge computing revolution. It enables cloud computing resources to be distributed across a wide range of locations, enabling faster processing of data and reduced latency.
Distributed cloud is particularly important for applications that require low latency, such as autonomous vehicles and gaming. By bringing the computing power closer to the device or application, edge computing can reduce the amount of time it takes for data to travel from the device to the cloud and back again.
Additionally, distributed cloud can improve the security of IoT devices. By processing and storing data locally, rather than sending it to a remote data center, sensitive data can be kept safe and secure.
Solution #2: Multi-Access Edge Computing
Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) is another key solution for the 5G and IoT edge computing revolution. It enables computing resources to be located at the edge of the network, closer to the device or application generating the data.
MEC is particularly important for applications that require low latency and high bandwidth, such as Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). By enabling computing resources to be located at the edge of the network, MEC can reduce the amount of time it takes for data to travel from the device to the cloud and back again, enabling faster and more immersive AR and VR experiences.
Additionally, MEC can improve the security of IoT devices. By processing and storing data locally, rather than sending it to a remote data center, sensitive data can be kept safe and secure.
Solution #3: Fog Computing
Fog computing is another key solution for the 5G and IoT edge computing revolution. It enables computing resources to be located at the edge of the network, closer to the device or application generating the data.
Fog computing is particularly important for applications that require low latency and high bandwidth, such as video streaming and gaming. By enabling computing resources to be located at the edge of the network, fog computing can reduce the amount of time it takes for data to travel from the device to the cloud and back again, enabling faster and more immersive video streaming and gaming experiences.
Additionally, fog computing can improve the security of IoT devices. By processing and storing data locally, rather than sending it to a remote data center, sensitive data can be kept safe and secure.
Solution #4: Private 5G Networks
Private 5G networks are another important solution for the 5G and IoT edge computing revolution. They enable organizations to build their own private 5G networks, providing faster and more secure connectivity for IoT devices.
Private 5G networks are particularly important for organizations that require a high level of security, such as government agencies and financial institutions. By building their own private 5G networks, organizations can ensure that data is kept secure and that there is no risk of interference or disruptions from other networks.
Additionally, private 5G networks can enable faster and more reliable communication between IoT devices, improving the overall efficiency and effectiveness of IoT deployments.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a critical technology for the 5G and IoT revolution, enabling faster decision-making, reduced latency and increased security. Distributed cloud, multi-access edge computing, fog computing and private 5G networks are all key solutions that organizations can use to take advantage of the benefits of edge computing. As the 5G and IoT revolution continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions in the future.





